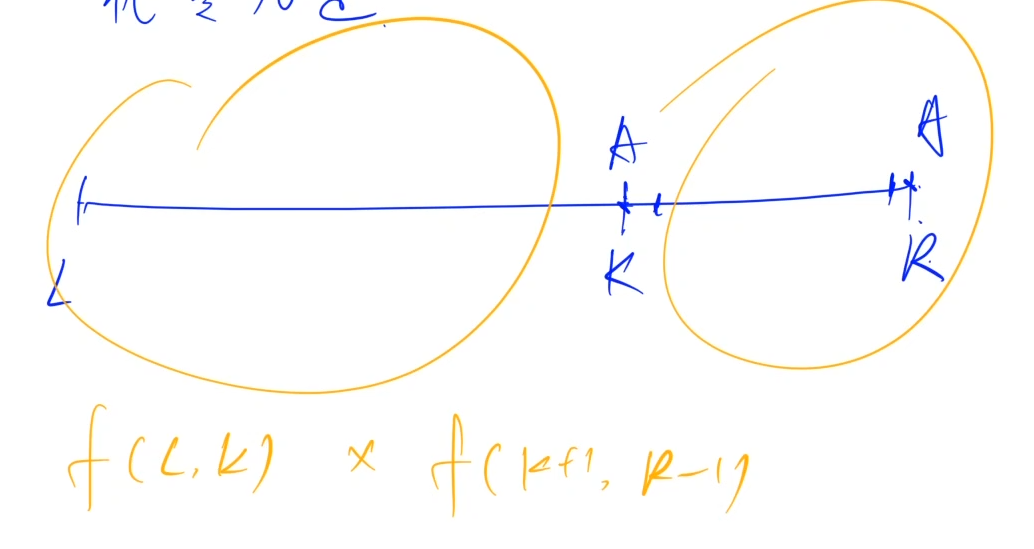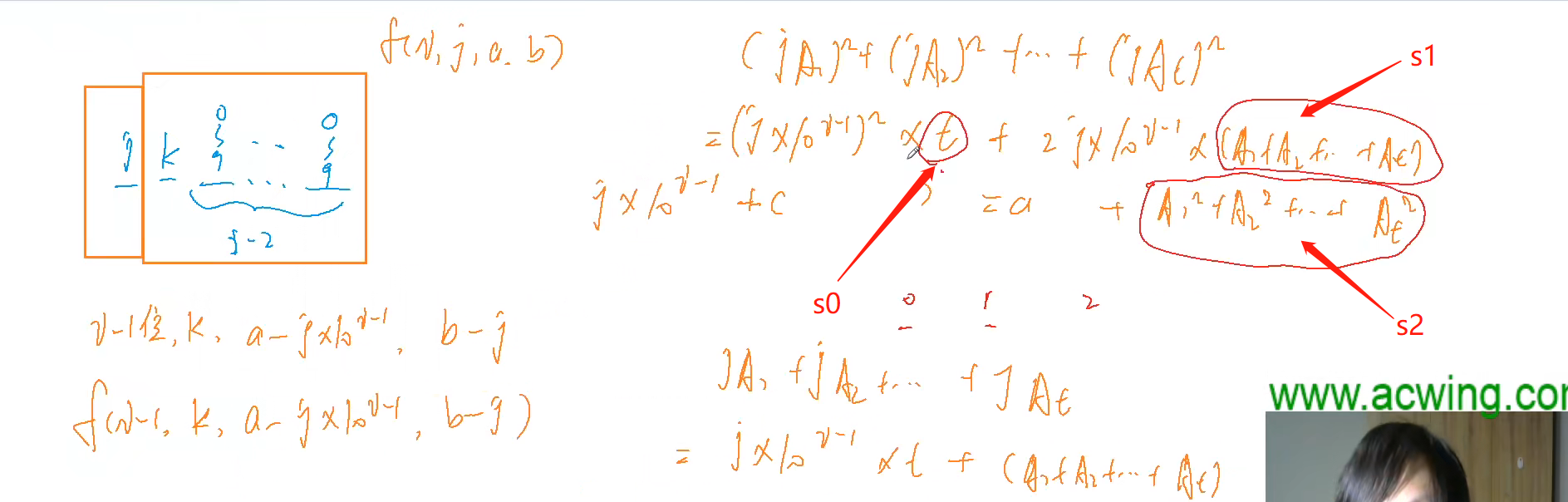Algorithm Note
Algorithm Note
DP(Dynamic Programming)
分类:
1.线性 dp
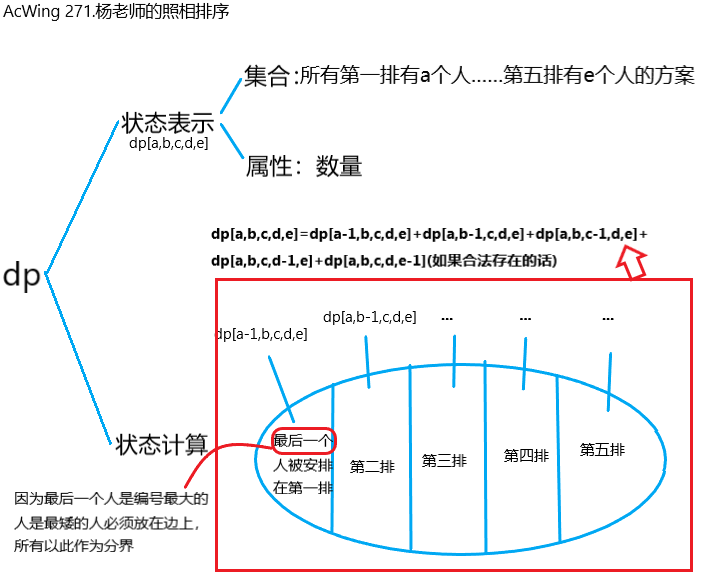
Question:AcWing 271.杨老师的照相排列
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/273
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆Tr
Question Analysis:
① 在每一排中,当前排好位置的人一直在最左边连续的位置。
② 从上到下(第一排到最后一排),每排人数单调递减。
③ 闫氏 dp 分析法
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=31;
int k;
long long dp[N][N][N][N][N];//必须用long long否则会爆栈
int res[5];
int main()
{
//dp process
while(cin >> k , k )
{
memset(res,0,sizeof res);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
cin >> res[i];
}
//dp process
memset(dp,0,sizeof dp);
dp[0][0][0][0][0]=1;
for (int a = 1; a <= res[0]; a++)//第一排
for (int b = 0; b <= min(res[1],a); b++)//第二排
for (int c = 0; c <= min(res[2],b); c++)////第三排
for (int d = 0; d <= min(res[3],c); d++)//第四排
for (int e = 0; e <= min(res[4],d); e++)//第五排
{
dp[a][b][c][d][e]=dp[a-1][b][c][d][e]+dp[a][b-1][c][d][e]+dp[a][b][c-1][d][e]+dp[a][b][c][d-1][e]+dp[a][b][c][d][e-1];//无需判断是否合法,因为不合法状态的值为0
}
cout << dp[res[0]][res[1]][res[2]][res[3]][res[4]] << endl;
}
}
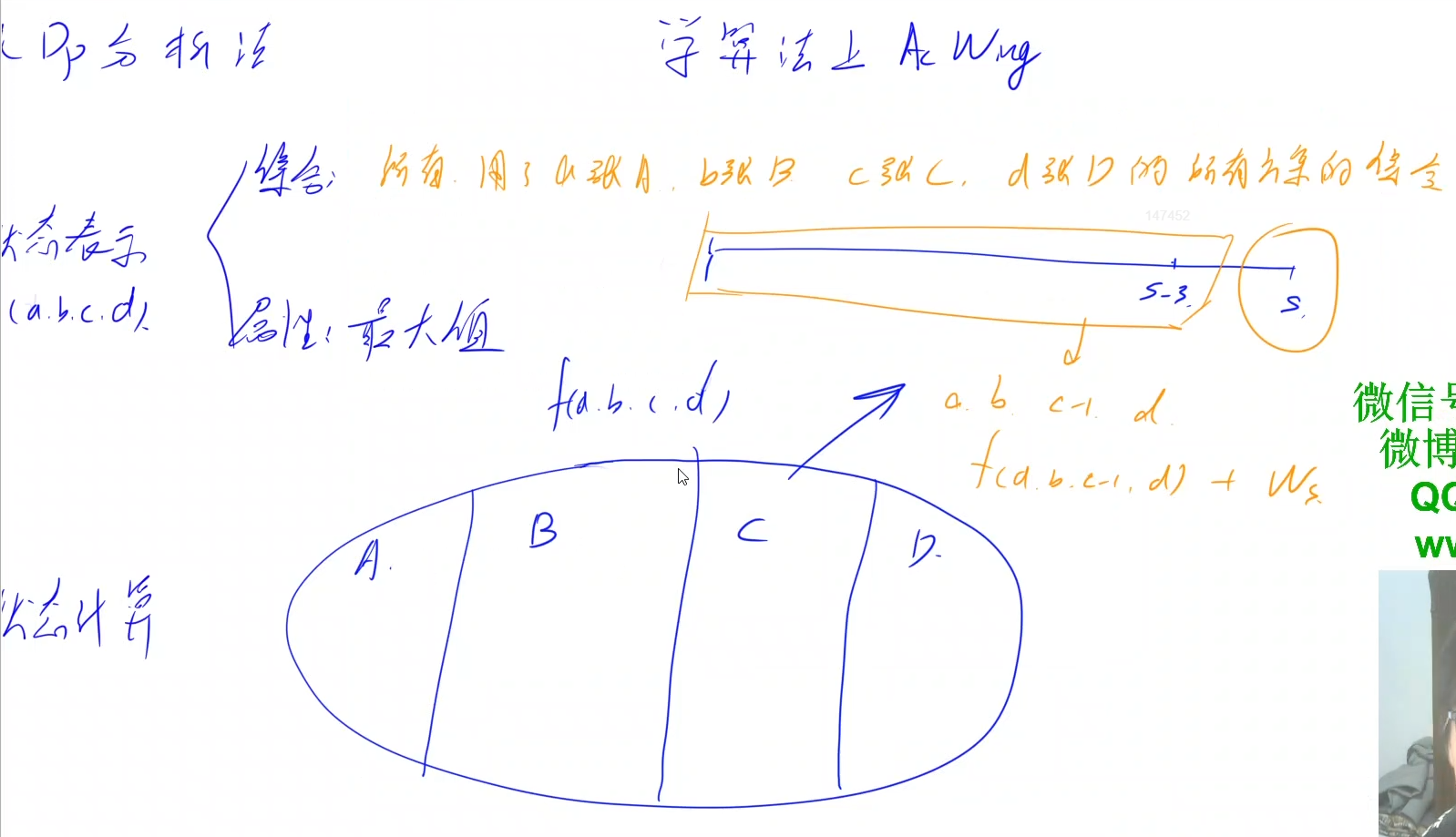
Question:AcWing 312.乌龟棋
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/314
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
Photo Above Tips: A=1,B=2,C=3,D=4,状态计算中 ABCD 均为最后一张取得是 ABCD
Attention:When there is no card at the beginning, your location is 1,your score is path[0+1]
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=355,M=41;
int n,m;
int path[N];//Donot Use path[0]
int dp[M][M][M][M];
int main()
{
int kind[5]={0};
cin >> n >> m ;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> path[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int temp;
cin >> temp;
kind[temp]++;
}
//dp process
for (int a = 0; a <= kind[1]; a++)
for (int b = 0; b <= kind[2]; b++)
for (int c = 0; c <= kind[3]; c++)
for (int d = 0; d <= kind[4]; d++)
{
int t=path[a+b*2+c*3+d*4+1];//因为第一格是起点,所以 例如当a=0,b=0,c=0,d=0时应该在第一格 故+1
auto &v=dp[a][b][c][d];
v=t;//if a,b,c,d不存在
if(a) v=max(v,dp[a-1][b][c][d]+t);
if(b) v=max(v,dp[a][b-1][c][d]+t);
if(c) v=max(v,dp[a][b][c-1][d]+t);
if(d) v=max(v,dp[a][b][c][d-1]+t);
}
cout << dp[kind[1]][kind[2]][kind[3]][kind[4]] << endl;
return 0;
}
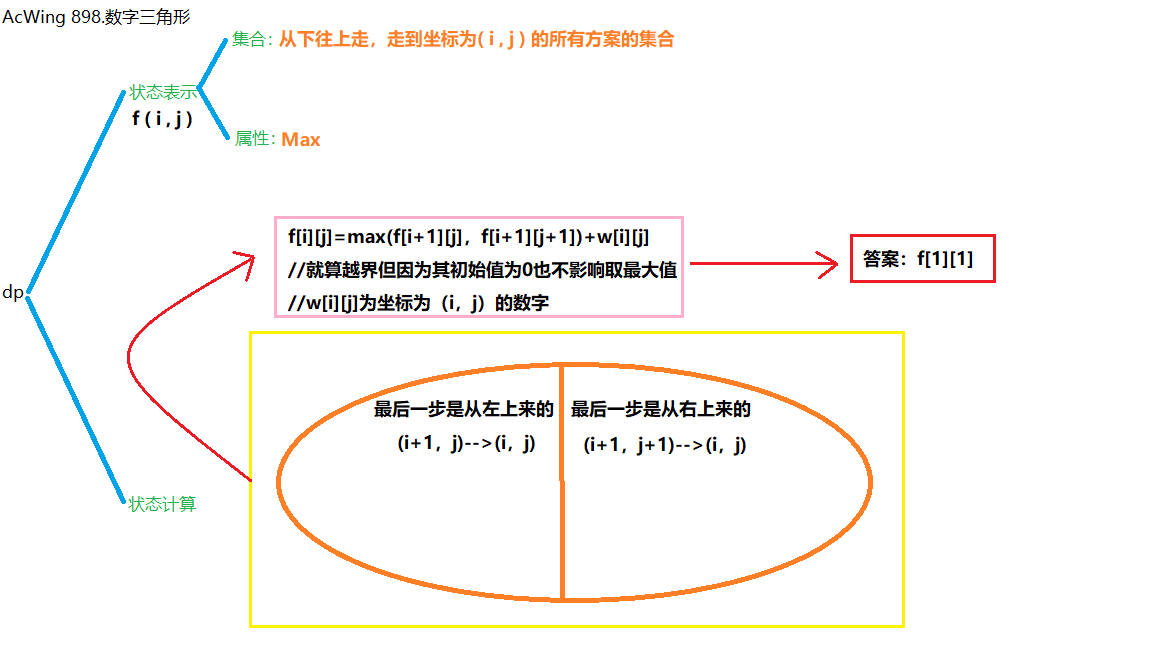
Question:AcWing 898.数字三角形
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/900
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆ ★★★★★ in the last century
Question Analysis:
若从上往下考虑,需要添加特判(是否越界等等…),所以采用从下往上考虑的方法
状态表示及状态转移方程见下图
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=510;
int f[N][N],w[N][N];
int n;
int main()
{
//initialize
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)//line
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)//row
{
cin >> w[i][j];
f[i][j]=w[i][j];
}
}
//dp process
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
f[i][j]=max(f[i+1][j],f[i+1][j+1])+w[i][j];//就算越界但因为其初始值为0也不影响取最大值
}
}
cout << f[1][1] << endl;
return 0;
}
Question:AcWing 895. 最长上升子序列
Question Link:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/897/
Question Difficulty Level:☆☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, f[N], w[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
cin >> w[i];
f[i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++ )
if(w[j] < w[i])
f[i] = max(f[i], f[j] + 1);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
res = max(res, f[i]);
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
Question:AcWing 897. 最长公共子序列
Question Link:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/899/
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m, f[N][N];
string a, b;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> a >> b;
a = " " + a;
b = " " + b;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
{
if(a[i] != b[j]) f[i][j]=max(f[i - 1][j],f[i][j - 1]);
else f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
}
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}
Question:AcWing 902. 最短编辑距离
Question Link:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/904/
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m, f[N][N];
string a, b;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> a;
a = " " + a;
cin >> m >> b;
b = " " + b;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i ++ ) f[0][i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) f[i][0] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
{
f[i][j] = min(f[i - 1][j] + 1, f[i][j - 1] + 1);
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - 1] + (a[i] != b[j]));
}
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}
2.区间 dp
顾名思义,区间 DP 即为在区间上求解最优值(DP)的问题
区间 DP 的主要思想就是先对小区间进行求解,然后再利用小区间的最优解合并求得大区间的最优解
区间 DP 一般是 dp[L][R] (左右端点)
一般循环方式为首先枚举区间长度,枚举左端点算出右端点
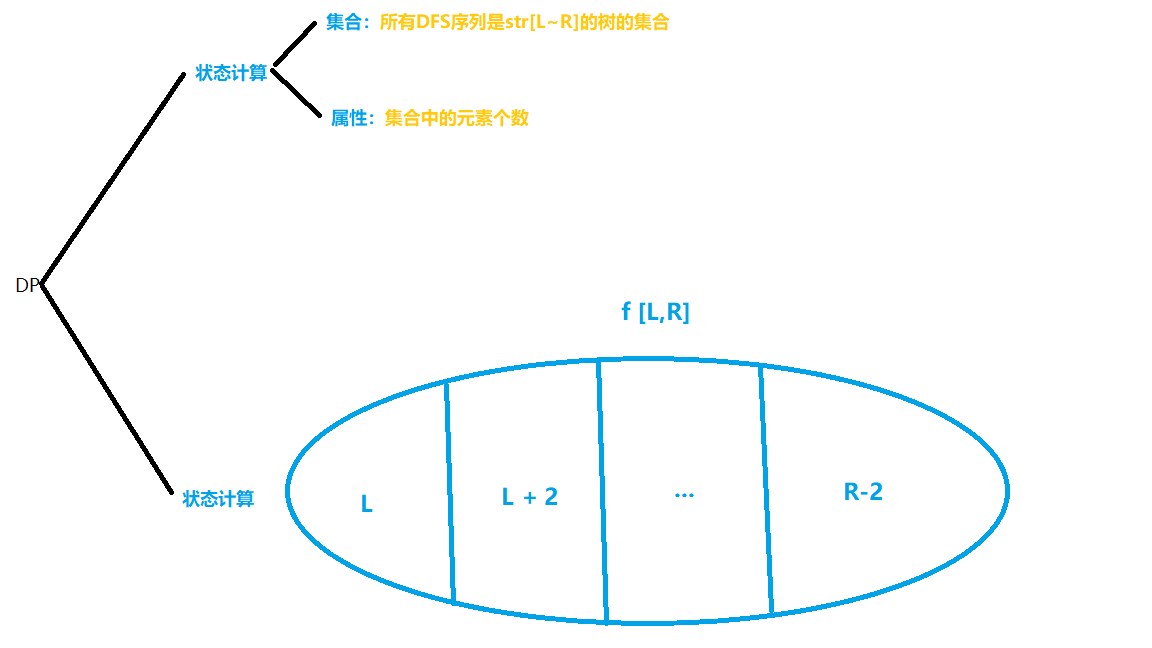
Question:AcWing 284. 金字塔
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/286
Question Analysis:
闫氏 DP 分析法:
枚举最后一棵子树
\[f [ L ] [ R ]=f [ L ] [ R ]+f [ K+1 ] [ R-1 ] * f [ L ] [ K ]\]Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=310,mod=1e9;
string str;
int f[N][N];
int main()
{
cin >> str;
int n=str.size();
if(n%2==0) cout << 0 << endl;
else
{
for (int len = 1; len <= n; len+=2) //枚举长度
{
for (int l = 0; l+len-1 <= n; l++)//枚举左端点
{
int r=l+len-1;//右端点
if(len==1) f[l][r]=1;
else if(str[l]==str[r])
{
for (int k = l; k < r; k+=2)//枚举分界点
{
if(str[k]==str[r]) f[l][r]=(f[l][r]+(ll)f[l][k]*f[k+1][r-1])%mod;
}
}
}
}
cout << f[0][n-1] << endl;
}
}
Question:AcWing 284. 金字塔
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/286
Question Analysis:
Please Visit:WeChat/CSDN/AcWing
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=210;//环拆链
int dp[N][N],w[N];//DoNotUse w[0]
int e,n;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> w[i] ;
w[n+i]=w[i];
}
for (int len = 2; len <= n+1; len++)//len==2即为一个单个的珠子
{
for (int l = 1; l+len-1 <= 2*n; l++)
{
int r=l+len-1;
if(len==2)//就一个珠子
{
dp[l][r]=0;
continue;
}
for (int k = l+1; k < r; k++)
{
dp[l][r]=max(dp[l][r],dp[l][k]+dp[k][r]+w[l]*w[k]*w[r]);
}
}
}
int ans=0;
for (int l = 1; l <= n; l++) ans=max(ans,dp[l][l+n]);
cout << ans << endl;
}
Question:AcWing 282. 石子合并
Question Link:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/284/
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 310;
int n, s[N], f[N][N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> s[i], s[i] += s[i - 1];
for (int len = 2; len <= n; len ++)
for (int i = 1; i + len - 1 <= n; i ++ )
{
int l = i, r = i + len - 1;
f[l][r] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for (int k = l; k <= r; k ++ )
f[l][r] = min(f[l][r], f[l][k] + f[k + 1][r] + s[r] - s[l - 1]);
}
cout << f[1][n] << endl;
return 0;
}
3.状态压缩 dp
状态压缩基本特征:用二进制表示状态,用十进制存储状态。
- 用二进制表示状态,用十进制数存储状态;
- 用位运算筛选出合法状态;
- 用位运算判断状态转移的条件;
- 计算时每个类累加上一行的兼容类。
Question:AcWing 327. 玉米田
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/329
Question Analysis:
经典的二进制状态压缩 dp
首先枚举
每行的所有状态:
每行的合法状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
①行内合法: 如果(!(i&i>>1))为真,则i合法 //i的二进制不含相邻的1的时候成立
例如: i=5: i=101 i>>1=010 (i&i>>1)为假 !(i&i>>1)为真
②行间兼容: a为当前行状态,b为上一行状态,g[i]为当前行(a)的原始状态(可不可种)
如果(!(a&b)&&(a&g[i])==a))为真,则a,b兼容
例如: b:0 0 0 , 0 0 1 , 0 1 0 , 1 0 0 , 1 0 1
当前: a:0 0 0 , 0 0 1 , 0 1 0 , 1 0 0 , 1 0 1
原始: g[i]=g[a]= 1 1 0
③状态表示:f[i][a]表示已经种植前i行,第i行第a个状态时的方案数
④状态计算:f[i][a]=∑f[i-1,b]//a,b即上例中,进行遍历
⑤总方案数:ans=∑f[n][a]//最后一行,枚举所有方案a求和
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=14,mod=1e8;
int g[14];//DoNotUse[0],TakeDown Unfertiled Land
int m,n;
int cnt=0;//同一行的合法状态数
int f[14][1<<14];
int s[1<<14];//一行的合法状态集
int main()
{
cin >> m >> n ;//m lines n rows
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
int temp;
cin >> temp;
g[i]=(g[i]<<1)+temp;//保存各行的状态值
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < (1<<n); i++)//枚举一行所有的状态
{
if(!(i&i>>1)) s[cnt++]=i;//保存一行的合法状态,即行内合法
}
f[0][0]=1;//什么都不种
for (int i = 1; i <= m+1; i++)//枚举行
{
for (int a = 0; a < cnt; a++)//本行 合法方案
{
for (int b = 0; b < cnt; b++)//上行 合法方案
{
if((s[a]&g[i])==s[a]&&!(s[a]&s[b]))// a种在肥沃土地,a b 同列不同时为 1 (如果加上b种在肥沃土地可以减少一些计算)
f[i][a]=(f[i][a]+f[i-1][b])%mod;
}
}
}
cout << f[m+1][0] << endl;//相当于只在1~m行种植
return 0;
}
Question:AcWing 1065. 涂抹果酱
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1067
Question Analysis:
三种状态,三进制状态压缩 dp,
$dp[i][j]$表示第$i$行第$j$个状态的所有方案数
- 定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=6,Mod=1e6;
int n,m,k;
int pow3[N];
int dp[N][N*N*N];
int state[N*N*N];//状态
int kternary=0;//第k行用三进制存储的十进制状态
int ksign;//记录k所在的位置
int cnt=0;
- 行内合法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
bool checkinline(int x)
{
int temp=-1;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
if(temp==x%3) return false;
temp=x%3;
x=x/3;
}
return true;//CanBeInALine
}
- 行间兼容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
bool checkinrow(int x,int y)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
if(x%3==y%3) return false;
x=x/3;
y=y/3;
}
return true;
}
- 得到所有可行的状态
1
2
for (int i = 0; i <= pow3[m]; i++)
if(checkinline(i)) state[cnt++]=i;
并把该种状态在$state[i]$中的$i$定为$dp[ line ] [ state ]$ 中的 $state$;
- 把第 k 行状态转换为三进制,然后枚举所有可行状态,找到特定的那行(即第 k 行)对应的状态值(即 state[i]中的 i),若找不到则打印 0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int temp;
cin >> temp;
kternary=kternary+(temp-1)*pow3[m-i-1];
}
for (int i=0 ; i < cnt ; i++)
{
if(state[i]==kternary)
{
ksign=i;
break;
}
}
if(!ksign)
{
cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
- DP Process
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
for(int line = 1 ; line <= n ; line ++)
{
if(line==k)//为特定的那行
{
if(line==1) dp[line][ksign]=1 ; //如果特定的那行是第一行
else
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < cnt ; j++)
{
if(checkinrow(state[j],state[ksign])) dp[line][ksign]=(dp[line-1][j]+dp[line][ksign])%Mod;
}
}
else //不为特定的那行
{
for(int s = 0 ; s < cnt ; s++)//枚举第s种状态
{
if(line==1) dp[line][s]=1;
else
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < cnt ; j++)//枚举上一行的所有状态(即使上一行的有些状态并不可取,但是因为其值为0,并无大碍,只是影响效率)
{
if(checkinrow(state[s],state[j])) dp[line][s]=(dp[line][s]+dp[line-1][j])%Mod;
}
}
}
}
}
}
- GetAns
1
2
3
4
5
6
int ans=0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < cnt ; i++)
{
ans=(ans+dp[n][i])%Mod;
}
cout << ans << endl ;
- 有未知错误,但大致思路如此。
4.树形 dp
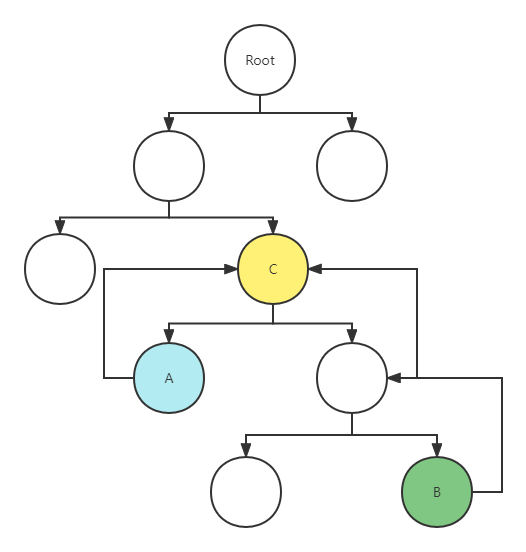
树形 DP 一般自底向上,将子树从小到大作为 DP 的“阶段”,将节点编号作为 DP 状态的第 1 维,代表以该节点为根的子树。
树形 DP 一般采用深度优先遍历,递归求解每棵子树,回溯时从子节点向上进行状态转移。在当前节点的所有子树都求解完毕后,才可以求解当前节点。
Question:AcWing 285. 没有上司的舞会
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/287
Question Analysis:
$f[i][0]$ 表示在以$i$为根的子树里面,不选择第$i$个点,能选出出来的最大快乐指数。 $f[i][1]$ 表示在以$i$为根的子树里面,选择第$i$个点,能选出出来的最大快乐指数。
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=6010;
int h[N],n;
int e[N],ne[N],w[N],idx;
//e[N]表示节点i的值是多少
//这是用于记录父子树之间关系的
int f[N][2];
bool st[N];//表示i号点有没有父节点
void add(int x ,int y)
{
e[idx]=y;
ne[idx]=w[x];
w[x]=idx++;
}
void dfs(int u)
{
f[u][0]=0;
f[u][1]=h[u];
for (int i = w[u]; ~i;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
dfs(j);
f[u][0]+=max(f[j][0],f[j][1]);
f[u][1]+=f[j][0];
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n ;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> h[i] ;
memset(w, -1, sizeof w);
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
{
int stu,bos;
cin >> stu >> bos;
add(bos,stu);
st[stu]=true;
}
//Get The FatherNode
int root=1;
while(st[root]) root++;
dfs(root);
cout << max(f[root][0],f[root][1]) << endl;
}
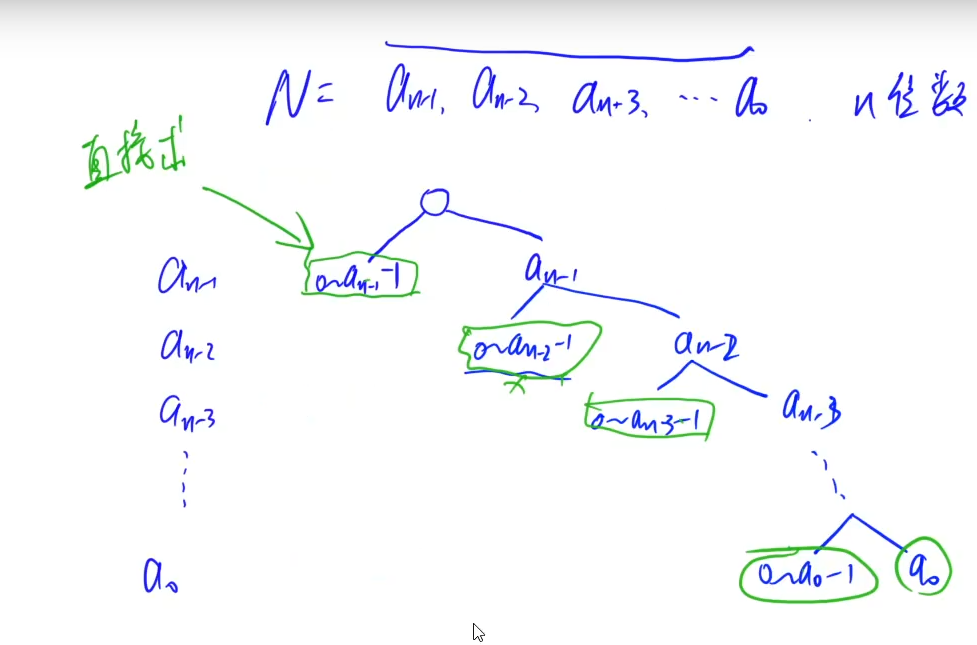
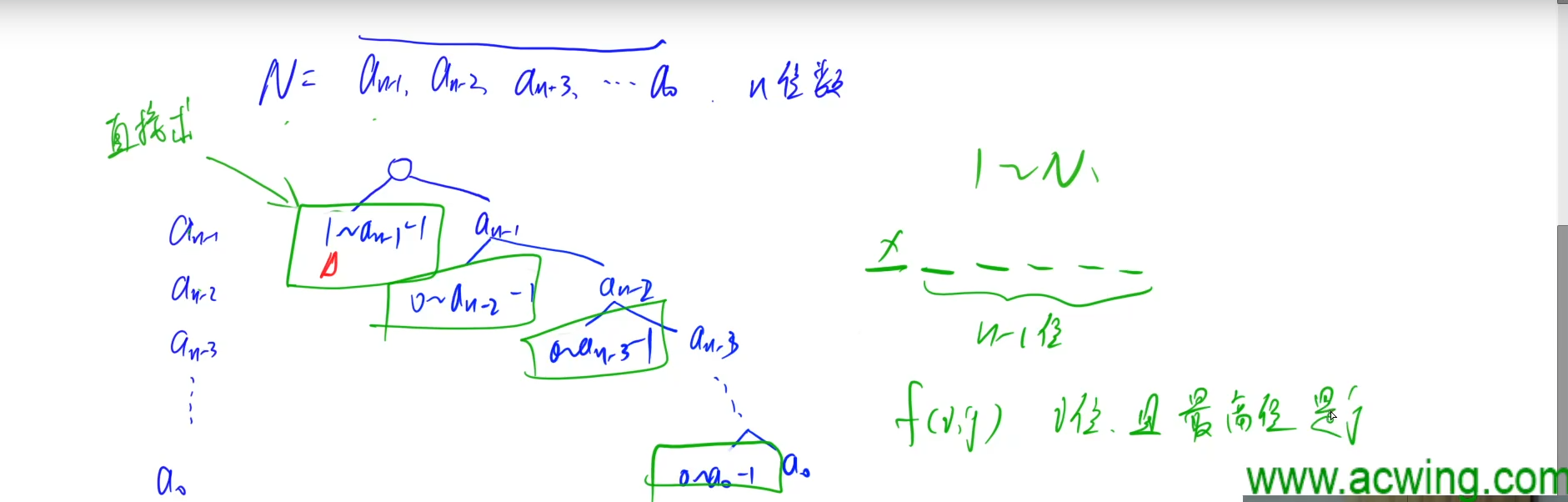
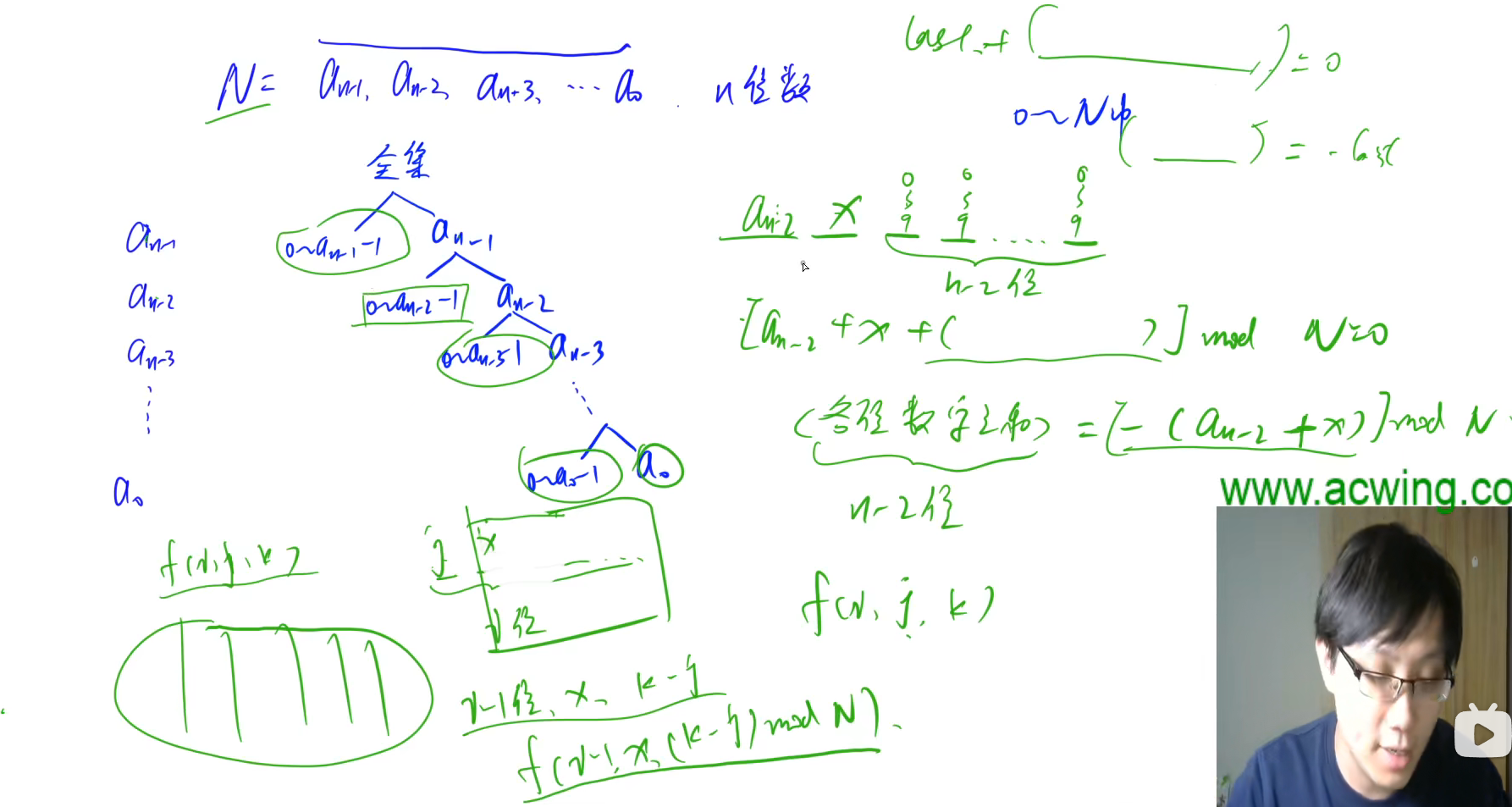
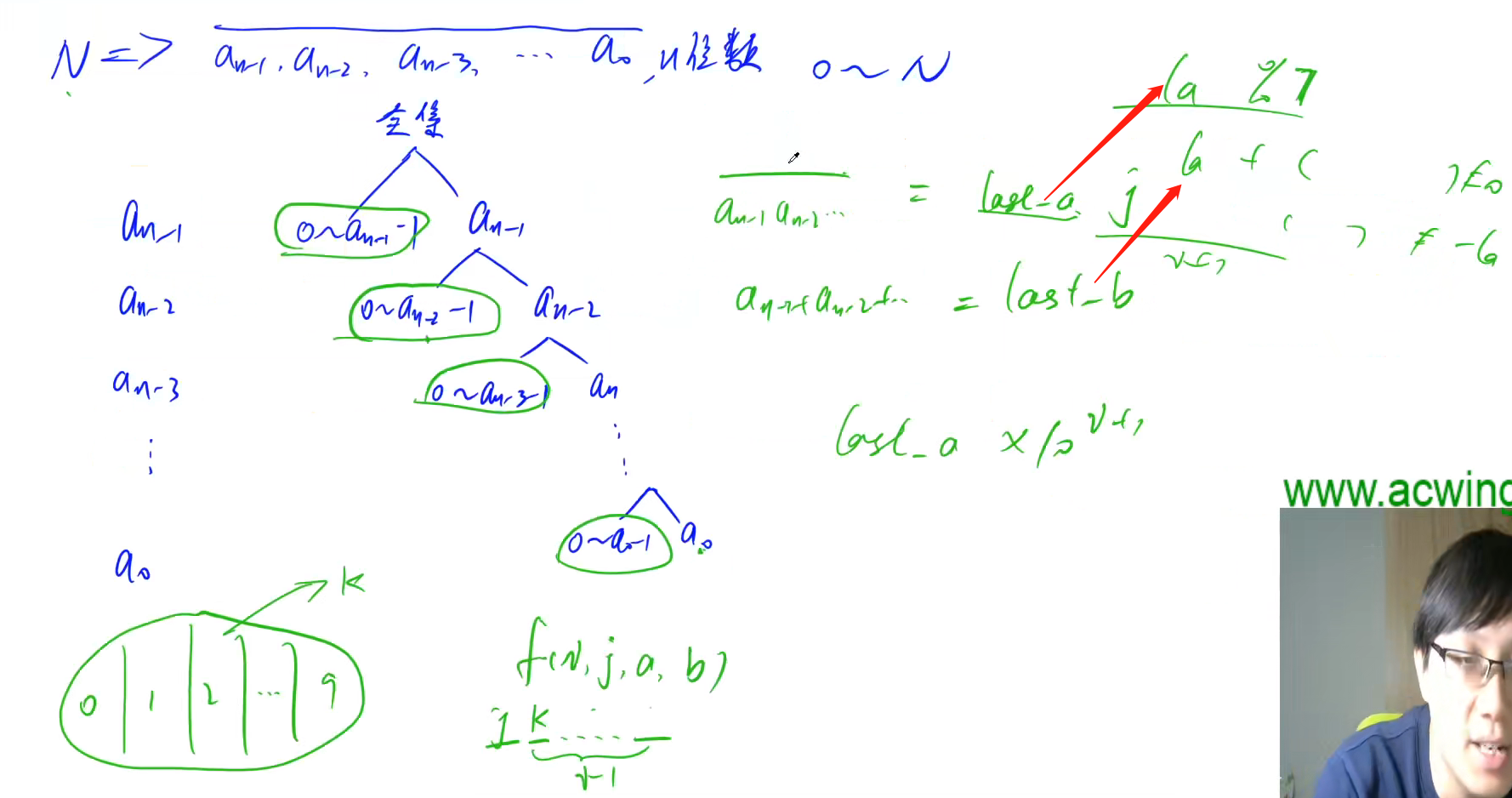
5.数位 dp
Kinds Difficulty Level:★★★★★
技巧:
把求在 [ X , Y ] 满足某种性质的数的个数,变成只有一个界限。
例:用 F(N)来表示 1~N 中满足某种性质的数的个数 , 那么 求在 [ X , Y ] 满足某种性质的数的个数为 F(Y)-F(X-1)
多从树的角度来考虑
More details in Video BV1yT4y1u7jW/
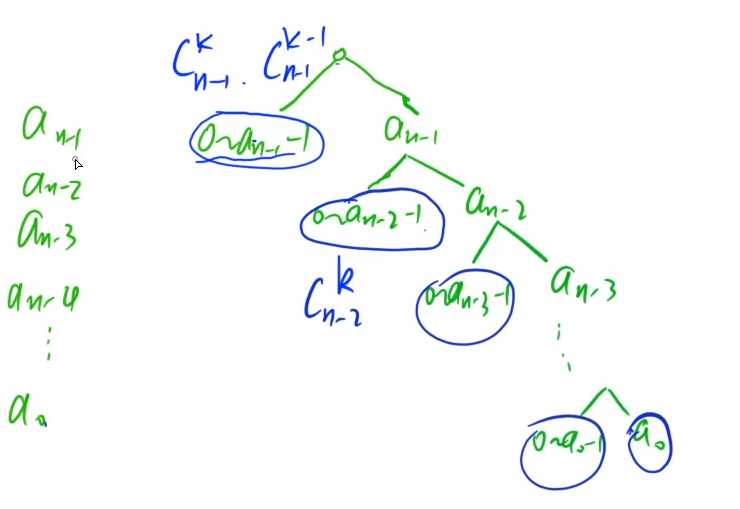
Question:AcWing 1081.度的数量
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1083
Question Difficulty Level:★★★☆☆
Question Description:
Question Analysis:
把每位数字抠出
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N=35;
int f[N][N];//f[i][j]表示从i个里选j个的所有方案数
int K,B;
int dp(int n)//return the suitable value kinds in range of [0,n] 返回可行的方案数
{
//判断边界
if(!n) return 0;
vector<int> nums;//将n的每一位抠出来放到nums
while(n) nums.push_back(n%B),n/=B;
int res=0,last=0;//last 表示前缀信息,表示前面已经有多少个1(每题含义不同),res为答案
for (int i = nums.size()-1; i >= 0; i--)//从最高位开始枚举
{
int x=nums[i];
if(x)// 左面的分支
{
res+=f[i][K-last];
if(x>1)
{
if(K-last-1>=0) res+=f[i][K-last-1];
break;
}
else //进入右面分支
{
last++;
if(last > K) break;
}
}
}
if(!i&&last==K) res++;//最右侧分支上的方案
return res;
}
int main()
{
//initialize
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
if(!j) f[i][j]=1;
else f[i][j]=f[i-1][j]+f[i-1][j-1];
}
}
int l,r;
cin >> l >> r >> K >> B ;
cout << dp(r)-dp(l-1) << endl;
}
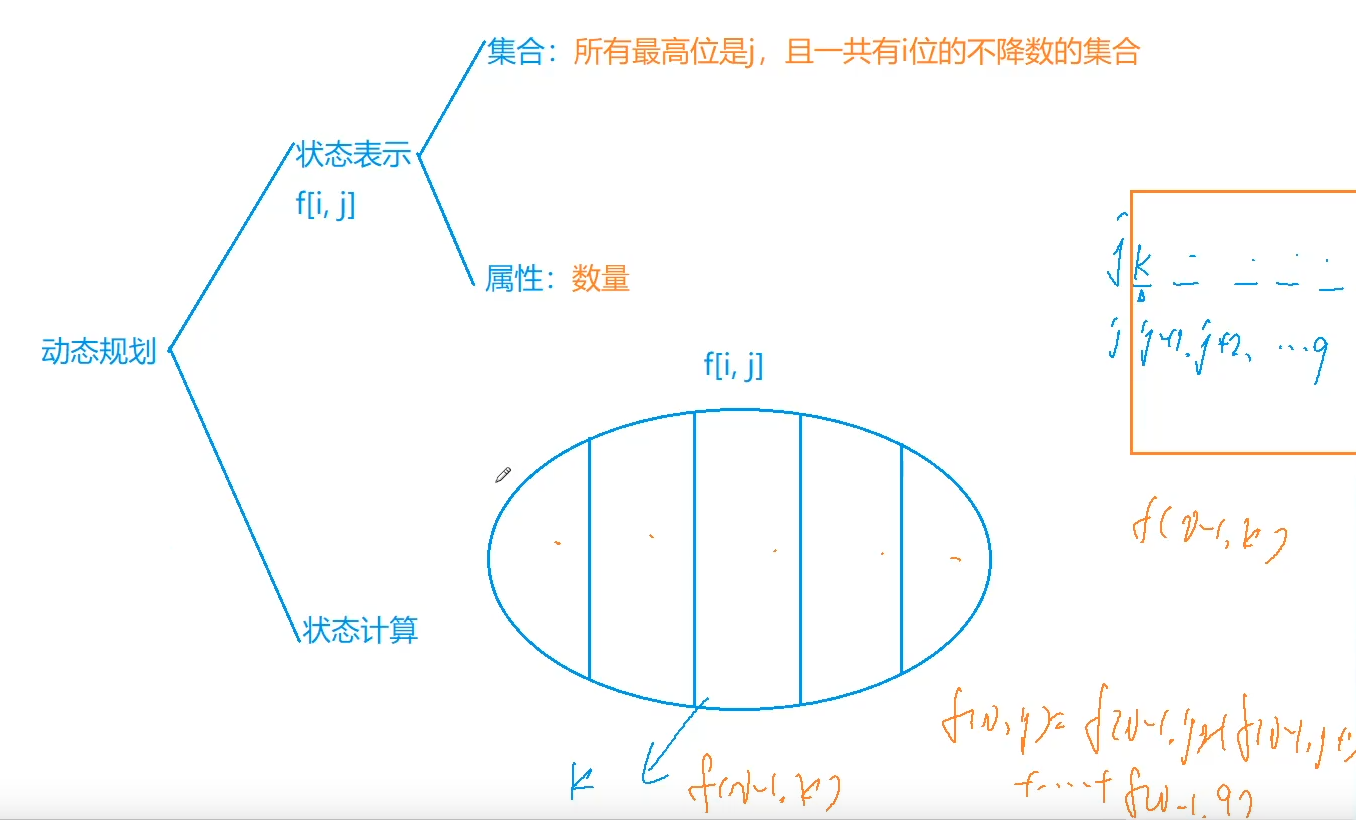
Question:AcWing 1082.数字游戏
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1084
Question Difficulty Level:★★★☆☆
Question Description:
Question Analysis:
dp Process to get all
Combination Process to get the count in the range
左面的直接可以求出(init)
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N=15;
int f[N][N]; // f[i][j]表示一共有i位,且最高位填j的所有方案数
void init()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) f[1][i]=1;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= 9; j++)
for (int k = j; k <= 9; k++)
f[i][j]+=f[i-1][k];
}
int dp(int n)//[0,n]里满足要求的数的数量 返回可行的方案数
{
if(!n) return 1;//边界 n=0时
vector<int> nums;
while(n) nums.push_back(n%10) , n/=10;
int res=0;
int last=0;//前缀信息,本题为上一位数
for (int i = nums.size()-1; i >= 0; i--)//从最高位开始遍历
{
int x=nums[i];
for (int j = last; j < x; j++)//最高位填 0~a[n-1]-1 的数
res+=f[i+1][j];
if(x<last) break;
last=x;
if(!i) res++;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
init();
int l,r;
while(cin >> l >> r) cout << dp(r) - dp(l-1) << endl;
return 0;
}
Question:AcWing 1083.Windy 数
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1085
Question Difficulty Level:★★★☆☆
Question Description:
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N=11;
int f[N][10];//f[i][j]表示一共有i位,且最高位填j的所有方案数
void init()
{
for (int i = 0; i <=9 ; i++) f[1][i]=1;//1~9
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++)//2位数开始看
for (int j = 0; j <= 9; j++)
for (int k = 0; k <= 9; k++)
if(abs(j-k)>=2) f[i][j]+=f[i-1][k];
}
int dp(int n)//返回可行的方案数
{
if(!n) return 0;
vector<int> nums;
while(n) nums.push_back(n%10),n/=10;
int res=0;
int last=-2;//记录上一位数字
for (int i = nums.size()-1; i >= 0; i--)//从高到低枚举每一位
{
int x=nums[i];
for (int j = i==nums.size()-1 ; j < x; j++)
{
if(abs(j-last)>=2) last=x;
else break;
}
if(!i) res++;
}
//特殊处理有前导零的数
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++)
res+=f[i][j];
return res;
}
int main()
{
init();
int l , r;
cin >> l >> r;
cout << dp(r) - dp(l - 1) << endl;
}
Question:AcWing 1084.数字游戏 Ⅱ
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1086
Question Difficulty Level:★★★★☆
Question Description:
Question Analysis:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 12 , M=110;
int f[N][10][M];//f[i][j][k]有i位数字,最高位是j,取模后为k
int P;
int mod(int x,int y)//x%y
{
return (x % y + y) % y ;
}
void init()
{
memset(f,0,sizeof f);
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) f[1][i][i%P] ++ ;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= 9; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < P; k++)
for (int x = 0; x <= 9; x++)
f[i][j][k]+=f[i-1][x][mod(k-j,P)];
}
int dp(int n)
{
if(!n) return 1;
vector<int> nums;
while(n) nums.push_back(n%10),n/10;
int res=0;
int last=0;
for (int i = nums.size()-1; i >= 0; i--)//从高到低枚举每一位
{
int x=nums[i];
for (int j = 0; j < x; j++)//左面的情况
res+=f[i+1][j][mod(-last,P)];//last % ? = P => ? = mod(-last,P)
last+=x;//右面的情况
if(!i && last % P ==0) res++;//已经枚举到最后一位了
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int l,r;
while(cin >> l >> r >> P )
{
init();
cout << dp(r)-dp(l-1) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
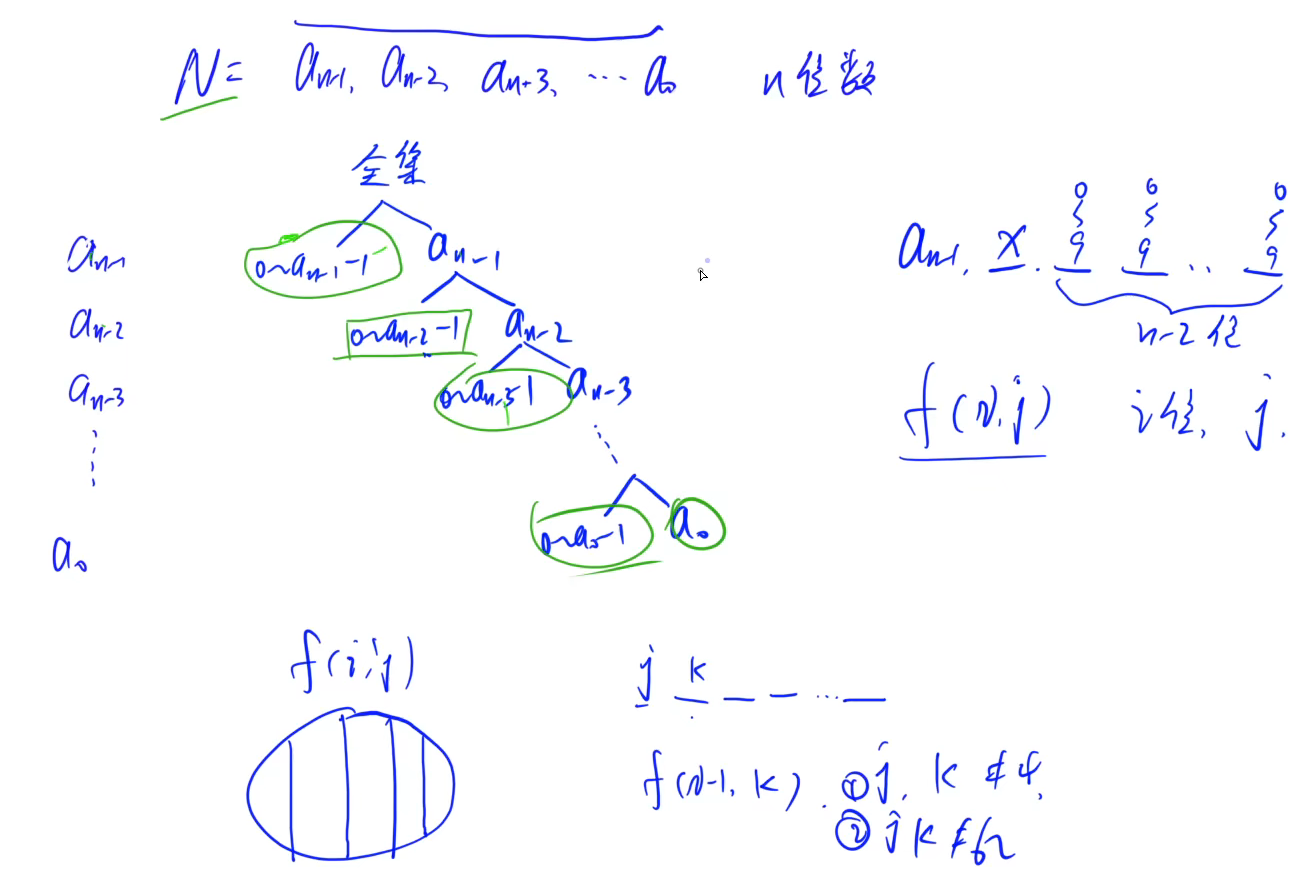
Question:AcWing 1085.不要 62
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1086
Question Difficulty Level:★★★★☆
Question Description:
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N=9;
int f[N][10];//f[i][j]有i位数字,最高位是j,且不包含4和64这种数的数量
void init()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) if(i!=4) f[1][i]=1
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= 9; j++)
{
if(j==4) continue;
for (int k = 0; k <= 9; k++)//次高位
{
if(k==4|| j==6&&k==2 ) continue;
f[i][j]+=f[i-1][k];
}
}
}
}
int dp(int n)
{
if(!n) return 1;
vector<int> nums;
while(n) nums.push_back(n%10),n/=10;
int res=0;
int last=0;//上一位数字
for (int i = nums.size()-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
int x=nums[i];
for (int j = 0; j < x; i++)//左分支
{
if(j==4 || last==6&&j==2) continue;
res+=f[i+1][j];
}
if(x==4 || last=6&&x==2) continue;//右分支
last=x;
if(!i) res++;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
init();
int n,m;
/*
while(cin >> n >> m )
{
if(!n&&!m) return 0;
else cout << dp(m)-dp(n-1) << endl;
}
*/
//<==>
while(cin >> n >> m , n || m ) cout << dp(m)-dp(n-1) << endl;
return 0;
}
Question:AcWing 1081.恨 7 不成妻
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1088
Question Difficulty Level:★★★★★
Question Description:
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
//Too hard to continue!
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=20 , P=1e9+7;
// int f[N][10][7][7];
struct F
{
int s0,s1,s2;
}f[N][10][7][7];
//f[i][j][a][b] 表示 一共有i位,最高位填的是j,这个数本身%7为a,这个数各位数之和%7为b
int pow7[N],pow9[N];
int mod(LL x,int y)//得到非负余数
{
return (x%y + y)%y;
}
void init()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
if(i==7) continue;
auto &v = f[1][i][i%7][i%7];
v.s0++;
v.s1+=i;
v.s2+=i*i;
}
LL power=10;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++,power*=10)
for (int j = 0; j <= 9; j++)
{
if(j==7) continue;
for (int a = 0; a < 7; a++)
for (int b = 0; b < 7; b++)
for (int k = 0; k <= 9; k++)
{
auto &v1=f[i][j][a][b] , &v2=f[i-1][k][mod(a-j*(power%7),7)][mod(b-j,7)];
v1.s0=(v1.s0+v2.s0)%P;
v1.s1=(v1.s1+j*(power%P)%P*v2.s0+v2.s1)%P;
v1.s2=(v1.s2+j*j*(power%P)%P*(power%P)%P*v2.s0%P+2*j*(power%P)%P*v2.s1%P+v2.s2)%P;
}
}
pow7[0]=pow9[0]=1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
pow7[i]=pow[i-1]*10%7;
pow9[i]=pow9[i-1]%10%P;
}
}
F get(int i,int j,int a,int b)
{
int s0=0,s1=0,s2=0;
for (int x = 0; x < 7; x++)
{
}
}
int dp(int n)
{
if(!n) return 0;
vector<int> nums;
while(n) nums.push_back(n%10),n/=10;
int res=0;
LL last_a=0,last_b=0;
for (int i = nums.size()-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
int x=nums[i];
for (int j = 0; j < x; j++)
{
if(j==7) continue;
int a=mod(-last_a*pow7[i+1],7);
int b=mod(-last_b,7);
auto v =get(i+1,j,a,b);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T ;
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++)
{
int l , r ;
cin >> l >> r ;
cout << mod(dp(r) - dp(l-1),P) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
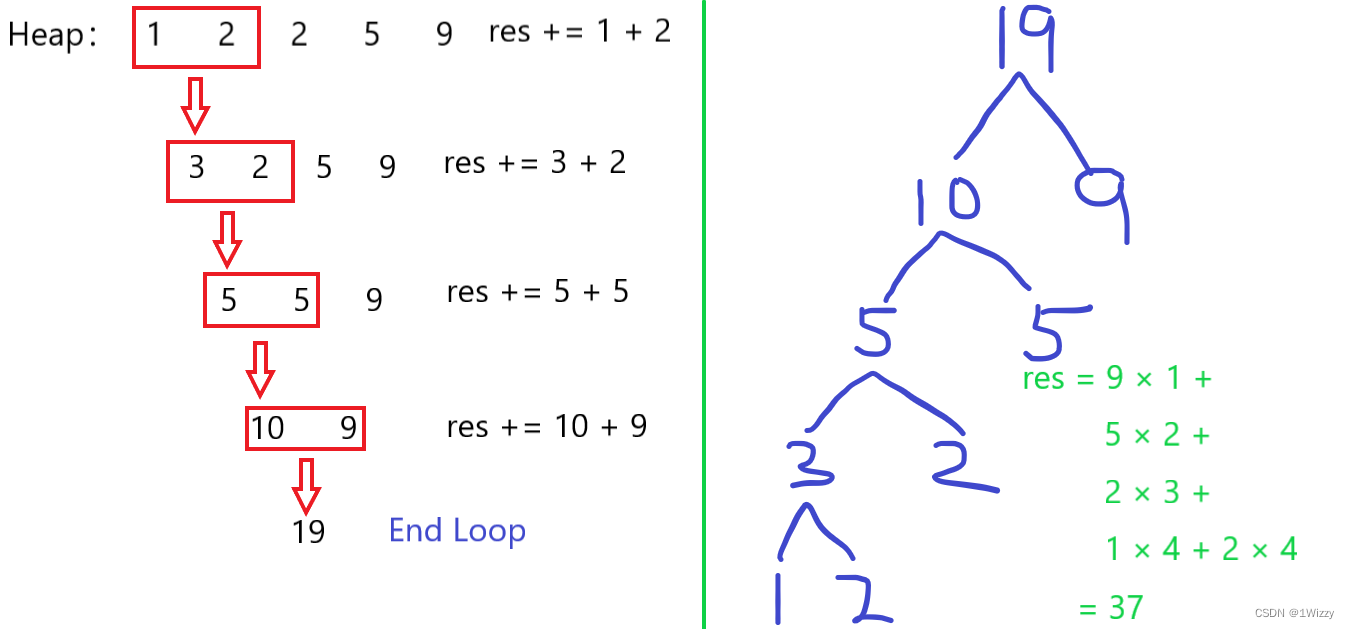
6.计数 dp
Question:AcWing 900. 整数划分
Question Link:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/902/
Question Analysis:
Code:
三重循环暴力,时间复杂度$O(n^2logn)$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010, Mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, f[N][N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) f[i][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) // 第 i 个物品
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) // 总容量
for (int k = 0; j - k * i >= 0; k ++ )// 有 k 个 第 i 个物品
f[i][j] = (f[i - 1][j - k * i] % Mod + f[i][j]) % Mod;
cout << f[n][n] << endl;
}
背包九讲
01 背包问题
Question Link: 2. 01 背包问题 - AcWing 题库
Question Analysis:
Code:
朴素版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int v[N], w[N], f[N][N];
int n, m;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
// consider f[0][0 ~ m] whether or not suit
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
// You Need Make Sure j - v[i] is greater than 0
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], j >= v[i] ? f[i - 1][j - v[i]] + w[i] : 0);
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}
优化版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int f[N], v[N], w[N];
int n, m;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = m; j >= v[i]; j -- )
// 因为转移j时需要用到上次(j - 1) 所以需要从后向前转移
// 又因为最大值不含第 i 个商品在上一个循环已经确定故 j >= v[i] 即可
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
cout << f[m] << endl;
return 0;
}
完全背包问题
Question Link: 3. 完全背包问题 - AcWing 题库
Question Description:
有 $N$ 件物品和一个容量是 $V$ 的背包。每件物品只能使用一次。
第 i 件物品的体积是 $v_i$,价值是 $w_i$。
Question Analysis:
Code:
三重朴素版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int v[N], w[N], f[N][N];
int n, m;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
for (int k = 0; k * v[i] <= j; k ++ )
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - k * v[i]] + w[i] * k);
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}
二重公式优化版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int v[N], w[N], f[N][N];
int n, m;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
{
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
if(v[i] <= j) f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i][j - v[i]] + w[i]);
}
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}
一重状态表示维数优化版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int v[N], w[N], f[N];
int n, m;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = v[i]; j <= m; j ++ )
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
cout << f[m] << endl;
return 0;
}
多重背包问题
Question Link: 4. 多重背包问题 I - AcWing 题库
Question Analysis:
Code:
朴素版:时间复杂度$O(n^3)$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int v[N], w[N], s[N], f[N][N];
int n, m;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> v[i] >> w[i] >> s[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j ++ )
for (int k = 0; k <= s[i] && k * v[i] <= j; k ++ )
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - v[i] * k] + w[i] * k);
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}
二进制优化版:时间复杂度$O(nvlogs)$
我们将物品的数量用二进制进行表示拆分,通过选择拆分后的物品来达到原来的效果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 25000, M = 1010; // N = M * log(s)
int f[N], v[N], w[N];
int n, m;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int a, b, s;
cin >> a >> b >> s;// v w s
int t = 1;
while(t <= s)
{
cnt ++;
v[cnt] = a * t;
w[cnt] = b * t;
s -= t;
t *= 2;
}
if(s > 0)
{
cnt ++;
v[cnt] = a * s;
w[cnt] = b * s;
}
}
n = cnt;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = m; j >= v[i]; j -- )
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
cout << f[m] << endl;
return 0;
}
分组背包问题
Question Link: 9. 分组背包问题 - AcWing 题库
Question Analysis:
Code:
朴素版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int f[N][N], v[N][N], w[N][N];
int n, m, s[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
cin >> s[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= s[i]; j ++ )
cin >> v[i][j] >> w[i][j];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j ++ )
for (int k = 0; k <= s[i]; k ++ )
if(j - v[i][k] >= 0)
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - v[i][k]] + w[i][k]);
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}
按照以前优化的方式可以将状态表示优化成一维
一维优化版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int f[N], v[N][N], w[N][N];
int n, m, s[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
cin >> s[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= s[i]; j ++ )
cin >> v[i][j] >> w[i][j];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = m; j >= 0; j -- )
for (int k = 0; k <= s[i]; k ++ )
if(j - v[i][k] >= 0)
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i][k]] + w[i][k]);
cout << f[m] << endl;
return 0;
}
Model
数字三角形
最长上升子序列(Longest Incresing Subsequence)
Dynamic Programming Method
由当前状态向后面状态转移
Question: AcWing 4741. 魔法百合井
Question Link: 4741. 魔法百合井 - AcWing 题库
Question Analysis:
Key: 记录每次状态转移时的 Record(投 4Coins 的操作)相对困难,可以对于当前状态进行 Record+ 倍增操作(投 2Coins 的操作),进行向后转移
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, f[N];
int main()
{
memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof f);
f[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i ++)
{
f[i] = min(f[i], f[i - 1] + 1);
for (int j = 1; i * (j + 1) <= 100000; j ++ )
f[i * (j + 1)] = min(f[i * (j + 1)], f[i] + 4 + 2 * j);
}
int T;
cin >> T;
for (int t = 1; t <= T; t ++)
{
cin >> n;
cout << "Case #" << t << ": " << f[n] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
倍增思想
倍增法,意为成倍增长。 在进行递推时,如果状态空间很大,通常的线性递推无法满足时间与空间复杂度的要求,那么我们可以通过成倍(通常以 2 作为基底)增长的方式,它能够使线性的处理转化为对数级的处理,大大地优化时间复杂度。
2 的幂的优化
1
2^n=(1<<(n))
IDA*
一、概念
简单的说,IDA 算法就是迭代加深版的 A 算法
二、分析
设计一个估价函数$f(state)<=真实步数$
若 $当前步数 + f(state) > 上界$ 真实步数必然大于上界,可以提前退出
三、模板代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
bool dfs()
{
if(now_depth + f() > max_depth) return false;
}
int depth=0;
while(!dfs(0,depth)) depth++;
四、示例代码
Question:AcWing 180.排书
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/182
Question Analysis:
连续选择$k$个书,一共有$n-k+1$ 种选法,总共有$n-k$种放法,那么一共有 $(1514 + 1413 + … + 2*1)/2 = 560$ 种操作
暴力最坏时间复杂度$O(560^4)$
每次操作会断开三个连接,然后引入三个连接。即每次操作最多会将三个连接修正
判断$n-1$个连接中有多少个错误的连接,记为$tot$,若全部修正至少需要$[tot/3]$次操作。(‘[ ]’为上取正符号)
估价函数:在当前状态之下,最少进行多少次操作,才可以变成有序序列。即$f(state)=[tot/3]$
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
//Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/182/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=15;
int n,q[N];
int w[5][N];//辅助数组(交换用)
int f()
{
int tot=0;
for (int i = 0; i+1 < n; i++)
{
if(q[i+1]!=q[i]+1) tot++;
}
return (tot+2)/3; //即(tot/3)的上取整
}
bool check()
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(q[i]!=i+1) return false;//q[0]=1
}
return true;
}
bool dfs(int depth,int max_depth)
{
if(depth + f() > max_depth) return false;
if(check()) return true;
//拓展状态,搜索每个分支
for (int len = 1; len <= n; len++)//枚举长度
{
for (int l = 0; l+len-1 < n; l++)//枚举起点
{
int r=l+len-1;
for (int k = r+1; k < n; k++)//枚举放置位置(因为放在前面和后面对称等价,故规定放在后面)
{
memcpy(w[depth],q,sizeof q);
int x,y;
for(x=r+1,y=l;x<=k;x++,y++) q[y]=w[depth][x];//Diagram 2
for(x=l;x<=r;x++,y++) q[y]=w[depth][x];//Diagram 3
if(dfs(depth+1,max_depth)) return true;
memcpy(q,w[depth],sizeof q);
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> q[i] ;
}
int depth=0;
while(depth<5&&!dfs(0,depth)) depth++;//迭代加深
if(depth>=5) puts("5 or more");
else cout << depth << endl;
}
}
Diagram:
- 初始
- 将 $[ L , R ]$ 抽出来
- 把$[ R + 1 , K ]$补到前面去
- 把$[ L , R ]$插入位置
Question:AcWing 181.回转游戏
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/183
Question Analysis:
估价函数:把中间 8 个数中出现最多次数的出现次数记为 k ,每次操作最多会加入一个相同的数,即最多 8 - k 次。f(state) = 8 - k ;
剪枝:避免枚举和上次相反的操作
最小字典序:按照字典序进行搜索
打表设计:编号,把八种操作对应的这一列数存下
编号: 0 1
1
2 3
4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1
11 12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19
1
2
3
20 21
22 23
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=24;
int op[8][7]={
{0,2,6,11,15,20,22},
{1,3,8,12,17,21,23},
{10,9,8,7,6,5,4},
{19,18,17,16,15,14,13},
{23,21,17,12,8,3,1},
{22,20,15,11,6,2,0},
{13,14,15,16,17,18,19},
{4,5,6,7,8,9,10},
};
int opposite[8]={5,4,7,6,1,0,3,2};//记录反操作
int center[8]={6,7,8,11,12,15,16,17};
int q[N];
int path[100];
int f()
{
static int sum[4];
memset(sum ,0 ,sizeof sum);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) sum[q[center[i]]]++;
int s=0;
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) s=max(s,sum[i]);
return 8-s;
}
bool check()
{
for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++)
{
if(q[center[i]]!=q[center[0]]) return false;
}
return true;
}
void operate(int x)
{
int t=q[op[x][0]];
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) q[op[x][i]]=q[op[x][i+1]];
q[op[x][6]]=t;
}
bool dfs(int depth,int max_depth,int last)//last:last op
{
if(depth+f()>max_depth) return false;
if(check()) return true;
//拓展其他分支
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if(opposite[i]==last) continue;//剪枝
operate(i);
path[depth]=i;
if(dfs(depth+1,max_depth,i)) return true;
operate(opposite[i]);//返回状态
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
while(cin >> q[0],q[0])
{
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) cin >> q[i];
int depth=0;
while(!dfs(0,depth,-1)) depth++;
if(!depth) printf("No moves needed");//一步也不需要做
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) printf("%c",path[i]+'A');
}
cout << endl << q[6] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Question:AcWing 182.破坏正方形
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/184
Question Analysis:
对于初始状态:
边长为 $1$ 的正方形:$n^2$
边长为 $2$ 的正方形:$(n-1)^2$
…
边长为$n$的正方形:$1^2$
一共有 $(n(n+1)(2n+1))/6$ 个正方形
一共 $2n(n+1)$ 根火柴
Target:从现有的火柴中,最少选择多少根火柴,可以使得每个正方形中都被至少选择了一根火柴
重复覆盖问题 一般用 $Dancing\quad Links$ 数据结构解决
图形化
问题转换:
至少选择多少行,可以使得每一列至少有一个 1(选择一根火柴)
搜索顺序:
每次选择一个还没有被覆盖的正方形(选择最小的一个)(优化),枚举选择它上面的哪一根火柴。
估价函数:
枚举每个正方形,如果当前正方形还是完整的,那么删掉它的所有边,但是只记删除一次。(估价函数 >=真实值)
正方形边的序号:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N=61;
vector<int> square[N];//每个正方形所有的边
bool st[N];//每条边是否被用过
int n,m;
bool check(vector<int> &sq)//检测正方形是否是完整的
{
for (int i = 0; i < sq.size(); i++)
{
if(st[sq[i]]) return false;
}
return true;
}
int f()
{
static bool state[N];//全局变量,只会被开辟一次
memcpy(state,st,sizeof st);//由于要修改st的值,先保存到另一个
int res=0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
vector<int> &sq=square[i];
if(check(sq))
{
res++;
for (int j = 0; j < sq.size(); j++) st[sq[j]]=true;
}
}
memcpy(st,state,sizeof st);
return res;
}
bool dfs(int depth,int max_depth)
{
if(depth+f()>max_depth) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
vector<int> &sq=square[i];
if(check(sq))
{
for (int j = 0; j < sq.size(); j++)
{
int x=sq[j];//枚举选择第x个
st[x]=true;
if(dfs(depth+1,max_depth)) return true;
st[x]=false;//状态回溯
}
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
cin >> n ;
memset(st,0,sizeof st);
//得所有正方形的所有边的序号
m=0;
for (int len = 1; len <= n; len++)//长度
{
for (int a = 1; a+len-1 <= n; a++)//枚举起点
{
for (int b = 1; b+len-1 <= n; b++)
{
//得到该正方形的所有边的序号
square[m].clear();
int d=2*n+1;//公差
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)//枚举每条边,得到正方形的所有边的序号
{
square[m].push_back(1+(a-1)*d+b-1+i);
square[m].push_back(1+(a+len-1)*d+b-1+i);
square[m].push_back(n+1+(a-1)*d+b-1+i*d);
square[m].push_back(n+1+(a-1)*d+b-1+i*d+len);
}
m++;
}
}
}
//PreDestroy
int k=0;
cin >> k;
while (k--)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
st[x]=true;
}
int depth=0;
while(!dfs(0,depth)) depth++;
cout << depth << endl;
}
}
Question:AcWing 195.骑士精神
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/197
Question Analysis:
估价函数:位置不对的数量
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
char str[5][5];
char tar[5][5]={'1','1','1','1','1',
'0','1','1','1','1',
'0','0','*','1','1',
'0','0','0','0','1',
'0','0','0','0','0'};//目标状态
int stari,starj;//初始空白位置坐标
pair<int,int> dire[8];//八种跳法
int f()//估价函数:位置不对的数量(除空白处)
{
int res=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if(str[i][j]!=tar[i][j]&&str[i][j]!='*') res++;
}
}
return res;
}
bool check()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
if(str[i][j]!=tar[i][j]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool dfs(int depth,int depth_max,int x,int y)//x,y为当前空白处坐标
{
if(depth+f()>depth_max) return false;
if(check()) return true;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
int tx=x+dire[i].first,ty=y+dire[i].second;
if(tx>=5||tx<0||ty>=5||ty<0) continue;//剪枝
swap(str[x][y],str[tx][ty]);
if(dfs(depth+1,depth_max,tx,ty)) return true;
swap(str[x][y],str[tx][ty]);//状态回溯
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
//跳法赋值
dire[0].first=1;dire[0].second=2;
dire[1].first=1;dire[1].second=-2;
dire[2].first=-1;dire[2].second=2;
dire[3].first=-1;dire[3].second=-2;
dire[4].first=2;dire[4].second=1;
dire[5].first=2;dire[5].second=-1;
dire[6].first=-2;dire[6].second=1;
dire[7].first=-2;dire[7].second=-1;
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
cin >> str[i][j];
if(str[i][j]=='*')
{
stari=i;
starj=j;
}
}
}
int depth=0;
while(depth<=15&&!dfs(0,depth,stari,starj)) depth++;
if(depth>15) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << depth << endl;
}
}
区间合并
一、步骤
- 将所有区间按左端点从小到大排序
- 从左到右遍历每个区间,去维护一个当前区间 $[ L , R ]$
1) $l[i] =< R$ $R=max( R , r[i] )$; 2) $l[i] > R$ 则将 当前区间 $[ L , R ]$ 存下,然后维护$[ l[i] , r[i] ]$
二、时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
三、实例代码
Question:AcWing 422.校门外的树
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/424
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int l,m;
pair<int,int> seg[110];
vector< pair<int,int> > v;
int main()
{
int ans=0;
cin >> l >> m ;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
cin >> seg[i].first >> seg[i].second ;
}
sort(seg,seg+m);
int L=seg[0].first,R=seg[0].second;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i ++ )
{
if(seg[i].first<=R) R=max(R,seg[i].second);
else
{
pair<int,int> temp;
temp.first=L;
temp.second=R;
v.push_back(temp);
L=seg[i].first;
R=seg[i].second;
}
}
pair<int,int> temp;
temp.first=L;
temp.second=R;
v.push_back(temp);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i ++ )
{
ans+=v[i].second-v[i].first+1;
}
cout << l- ans +1<< endl;
}
快速幂(FastPow)
一、概念
顾名思义即快速计算幂的方法
二、原理
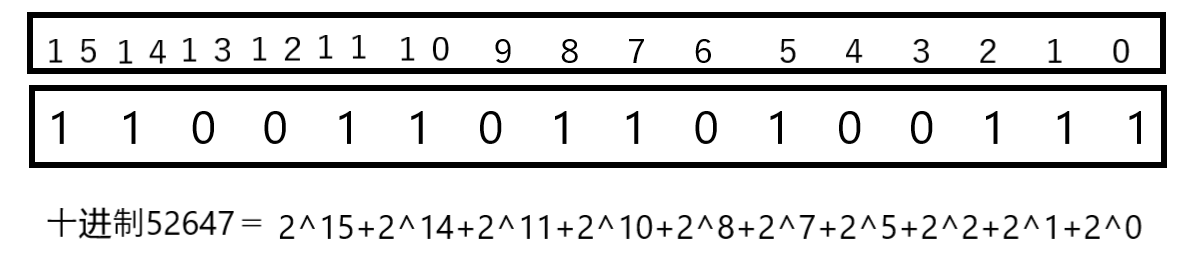
每个数均有二进制的表达方式,例如 十进制 52647 的 二进制 为 $1100 \ 1101\ 1010\ 0111$ 即 $2^{15}+2^{14}+2^{11}+2^{10}+2^8+2^7+2^5+2^2+2^1+2^0=52647$
三、模板代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
/*运用位运算符*/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int fastpow(int a,int n)
{
int ans=1;
while(n)
{
if(n&1) ans=ans*a;//n的最后一位是1,表示需要乘
a=a*a;//递推:a->a^2->a^3->a^4
n>>=1;//n右移4一位,把n的二进制最后一位去掉
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
cout << fastpow(3,2) << endl; //9
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
int fastpow(int m, int k, int p)
{
int res = 1 % p, t = m;
while (k)
{
if (k&1) res = res * t % p;
t = t * t % p;
k >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
Tips:$1 « n$等价于$2^n$
四、快速幂的拓展
快速幂采用了倍增的思想可以拓展至有结合律的运算
Question AcWing 205. 斐波那契
Question Link:205. 斐波那契 - AcWing 题库
Question Analysis:
\[\left[ \begin{matrix} fib_{n-1} & fib_n \\ 0 & 0 \\ \end{matrix} \right] \cdot \left[ \begin{matrix} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 \\ \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} fib_n & fib_{n+1} \\ 0 & 0 \\ \end{matrix} \right]\]其实部分只需
1x2的矩阵即可,但是在C++中需要写两个矩阵乘法函数,故全部记为2x2矩阵
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int Mod = 10000;
void mul(int a[][2], int b[][2])
{
int c[2][2] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j ++ )
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k ++ )
c[i][j] = (c[i][j] + a[i][k] * b[k][j]) % Mod;
memcpy(a, c, sizeof c);
}
int fib(int n)
{
int a[2][2] = {0, 1, 0, 0};
int f[2][2] = {0, 1, 1, 1};
while (n)
{
if (n & 1) mul(a, f);
mul(f, f);
n >>= 1;
}
return a[0][0];
}
int main()
{
int n;
while (cin >> n, n != -1)
cout << fib(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
默写测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
int qmi(int a, int k, int p)
{
int res = 1;
while (k)
{
if (k & 1) res = res * a % p;
a = (LL)a * a % p;
k >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
二分法
一、概念
二、模板代码
二分模板一共有两个,分别适用于不同情况。
算法思路:假设目标值在闭区间 $[ l , r ]$ 中, 每次将区间长度缩小一半,当 $l = r$ 时,我们就找到了目标值。
- 版本 1
当我们将区间 $[ l , r ]$ 划分成 $[ l , mid ]$ 和 $[ mid + 1, r ]$ 时,其更新操作是 $r = mid$ 或者 $l = mid + 1$ ;计算 $mid$ 时不需要加 $1$ .
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
int bsearch_1(int l, int r)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (check(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;//For Now l==r
}
- 版本 2
当我们将区间 $[ l , r ]$ 划分成 $[l,mid-1]$和 $[mid,r]$时,其更新操作是 $r=mid-1$ 或者 $l = mid$ 此时为了防止死循环,计算 $mid$ 时需要加 $1$ 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
int bsearch_2(int l, int r)
{
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if (check(mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return l;
}
Tips:
1
x >> 1 <=> x / 2
三、实例代码
Question:AcWing 422.校门外的树
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/424
Question Algorithm:
Question Analysis:
- 所有长度大于 $F$ 的连续子段 最大平均值 $Ave$
- 假设答案为 $Ave=Mid$ 进行二分判断 // 将最优化问题–> 判断问题
- 每一个数减去 $Mid$ 去检查是否存在长度大于$F$的连续子段,它的总和非负。即$sum[j]-sum[i] >=0$(i 为前指针,j 为后指针)<=>$sum[ j ] >= sum[ i ]$ 若存在则说明 $Mid <= Ave$ 否则 $Mid >= Ave$ 进行二分
- 最后输出答案 $(int)Ave*1000$
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=100005;
int n,m;//农场由n块地组成,至少需要m块地
int cows[N];
double sum[N];//前缀和DoNotUsesum[0]
bool check(double avg)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) sum[i]=sum[i-1]+cows[i]-avg;
double minv=0;
for (int i = 0,j = m; j <= n; i++,j++)
{
minv=min(minv,sum[i]);
if(sum[j]>=minv) return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> cows[i];
double l=0,r=2000;
while(r-l>1e-5)
{
double mid=(l+r)/2;
if(check(mid)) l=mid;
else r=mid;
}
cout << int(r*1000) << endl;
}
四、手写实现二分 STL
For the exam which cannot use STL;
Based on yxc’s template;
lower_bound
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// array is in ascending order
// return the index of the first element which is greater equal than val;
// Cannout Handle the situation that there is no element is greater equal than val, and in this situation, it will return the max index;
// To Handle this problem, you can set a sentinel(+inf) at the end of the array;
int LowerBound(int w[], int n, int val)
{
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (w[mid] >= val) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
upper_bound
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// array is in ascending order
// return the index of the first element which is greater than val;
// Cannout Handle the situation that there is no element is greater than val, and in this situation, it will return the max index;
// To Handle this problem, you can set a sentinel(+inf) at the end of the array;
int UpperBound(int w[], int n, int val)
{
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (w[mid] > val) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
Floyd
一、概念
Floyd 算法又称为插点法,是一种利用动态规划的思想寻找给定的加权图中多源点之间最短路径的算法,与 Dijkstra 算法类似。该算法名称以创始人之一、1978 年图灵奖获得者、斯坦福大学计算机科学系教授罗伯特·弗洛伊德命名。
二、特色
- 本算法边权可正可负
- 可以求任意两点间的最短路径
- 不允许有包含带负权值的边组成的回路
三、时间复杂度:$O(n^3)$
四、空间复杂度:$O(n²)$
五、模板代码
需要注意循环顺序不能变:第一层枚举中间点,第二层和第三层枚举起点和终点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
int d[N][N];//d[i][j]表示i->j的最小距离
memset(d,0x3f,sizeof d);
for(int i=0; i>N ; i++ ) d[i][i]=0;
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
in[j] = min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j]);
换言之:对于从 $i → j$ 存不存在一条更近的路经过 $k$ 中转而到达 $j$ 即:$i → k → j$
六、示例代码
Question:AcWing 1471.牛奶工厂
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1473
Question Algorithm:Floyd 枚举 图的遍历 传递闭包 思维题
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
用连通表进行存储图,因为本题只考察连通性,故用$Bool$类型数组即可。
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 105;
bool f[N][N];//存储是否连通
int n;
int main()
{
int res=-1;
memset(f, false, sizeof f);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ )
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
f[a][b]=true;
}
//Floyd Algorithm Core ↓↓↓↓↓
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k ++ )
{
f[j][k]=(f[j][k]||(f[j][i]&&f[i][k]));
}
//Floyd Algorithm Core ↑↑↑↑↑
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
{
if(j==i) continue;
if(f[j][i]) res=i;
else
{
res=-1;
break;
}
}
if(res==i) break;
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
Question:AcWing 1375.奶牛回家
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1377
Question Algorithm:最短路 Floyd
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
直接用 ASCII 码来存储(懒)
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N=128;
vector<char> v;
int g[N][N];g[i][j]表示i->j的最小距离in the end of the Code
int p;
pair<char,int> ans;
int main()
{
ans.second=0x3f3f3f3f;
memset(g,0x3f,sizeof g);
cin >> p;
for (int i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
char a,b;
int c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
g[(int)a][(int)b]=min(g[(int)a][(int)b],c);
g[(int)b][(int)a]=min(g[(int)a][(int)b],c);
if(a>='A'&&a<'Z') v.push_back(a);
if(b>='A'&&b<'Z') v.push_back(b);
}
for (int k = 1; k <= N; k++)
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
g[i][j] = min(g[i][j],g[i][k] + g[k][j]);
vector<char>::iterator it=v.begin();
for(;it!=v.end();it++)
{
if(ans.second>g[(int)*it]['Z'])
{
ans.second=g[(int)*it]['Z'];
ans.first=*it;
}
}
cout << ans.first << ' ' << ans.second << endl;
}
Dijkstra
一、概念
迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)是由荷兰计算机科学家狄克斯特拉于 1959 年提出的,因此又叫狄克斯特拉算法。是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有权图中最短路径问题。迪杰斯特拉算法主要特点是从起始点开始,采用贪心算法的策略,每次遍历到始点距离最近且未访问过的顶点的邻接节点,直到扩展到终点为止。
二、特色
- 本算法边权不可为负。
- 可以求出起点到任意点的最短路径及其路径。(路径需要特殊处理)
三、时间复杂度:朴素:$O(n²)$** 堆优化:**$O(mlog(n))$
四、空间复杂度:$O(n²)$
五、模板代码
- 朴素
- 图的存储——邻接矩阵 $g[a][b]$
- $dist[i]$:从 $1$ 号点到$i$号点的最短路径
- 算法流程:
初始化:$dist[原点]=0$,$dist[i]=+∞$,然后
伪代码:
1
2
3
4
5
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
(1)找出剩下点中距离原点最小的点 t
(2)用t号点更新其他点的距离
}
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=1010,INF=1000000000;
int g[N][N];//邻接矩阵
int dist[N];//每个点到起点的距离
bool st[N];//存储每个点的最短距离是否已确定
void dijkstra()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i ++ ) dist[i]=INF;//初始化距离
dist[1]=0;//第一个点到自身的距离为0
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)//迭代n次,每次可以确定一个点到起点的最短路
{
//找出剩下点中距离原点最小的点
int t=-1;//t是剩下点中距离原点最小的点
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(!st[j]&&(t==-1||dist[j]<dist[t])) t=j;
st[t]=true; //标记该点
// 用t更新其他点的距离
//从1号点到j号点的距离能否用经过t的一条路径来更新
//即1->j能否用1->t和t->j路径来更新
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
dist[j]=min(dist[j],dist[t]+g[t][j]);
}
}
int main()
{
//初始化图
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j <= N; j ++ )
g[i][j]=INF;
//输入图
/*Code*/
dijkstra();//调用函数
cout << dist[?] << endl;//输出起点到?的最短距离
}
- 堆优化
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=15e4+5,INF=999999999;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
//用邻接表去存图
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx;
int w[N];//存权重
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
int n,m;
void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
w[idx]=c;
e[idx]=b;
ne[idx]=h[a];
h[a]=idx++;
}
void dijkstra()
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) dist[i]=INF;
dist[1]=0;
priority_queue<PII,vector<PII>,greater<PII>> heap;//定义小顶堆
//顾名思义,本堆将自动从小到大排序,故堆顶即为没有确定最短距离的点且距离最小的点(及其距离)
heap.push({0,1});//dist[0],first=distance,second=PointLocation
while(heap.size())
{
PII k=heap.top();//取最小距离的点
heap.pop();//弹出
int loc=k.second,dis=k.first;
if(st[loc]) continue;//如果已经找到了最短距离则continue
st[loc]=true;
//常规遍历操作
for (int i = h[loc]; i != -1; i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];//i只是个下标,e中在存的是i这个下标对应的点
if(dist[j]>dis+w[i])
{
dist[j]=dis+w[i];
heap.push({dist[j],j});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);//初始化邻接表
cin >> n >> m ;//读入点和边
//初始化邻接表
/*Code*/ //调用add()
dijkstra();//调用函数
cout << dist[?] << endl;//输出起点到?的最短距离
}
六、实例代码
Question:AcWing 849.Dijkstra 求最短路 I
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/851
Question Algorithm:Dijkstra
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
对于数据范围:$1≤n≤500$,$1≤m≤10^5$, 图中涉及边长均不超过 $10000$ 仅仅用朴素的 Dijkstra 算法即可。参考 CodeOne
对于数据范围:$1≤n$,$m≤1.5×10^5$, 图中涉及边长均不小于 $0$,且不超过 $10000$。 数据保证:如果最短路存在,则最短路的长度不超过 $10^9$。应使用堆优化,参考 CodeTwo
由于本题是 AcWing Dijkstra 算法的模板题,故不做过多分析。
CodeOne Time Complexity:$O(n²)$
CodeTwo Time Complexity:$O(mlog(n))$
CodeOne:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=505,INF=999999;
int n,m;
int g[N][N];//存储距离
bool st[N];//存储每个点的最短距离是否已确定
int dist[N];//存储每个点到起点的距离
void dijkstra()
{
// memset(dist,INF,sizeof dist);//初始化距离 //初始化大值时会有错误,应使用for循环
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i ++ ) dist[i]=INF;
dist[1]=0;//第一个点到自身的距离为0
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)//进行n次迭代
{
int t=-1;//存储当前访问的点
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)//遍历每个点
{
//该步骤即寻找还未确定最短路的点中路径最短的点
if(!st[j]&&(t==-1||dist[t]>dist[j])) t=j;
}
st[t]=true;
//更新其余未确定点的最短距离 , 此处直接遍历不进行检查是否有连接
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
dist[j]=min(dist[j],dist[t]+g[t][j]);
//dist[t]是 还未确定最短路的点中路径最短的点 到起点的距离
//这时开始拓展t点附近未被确定的点 t->未被确定的点 的距离 为 g[t][j]
//将新值与原始值进行取小
}
}
}
int main()
{
// memset(g,INF,sizeof g);//初始化大值时会有错误,应使用for循环
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j <= N; j ++ )
g[i][j]=INF;
cin >> n >> m ;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
g[a][b]=min(c,g[a][b]);//若发生重边的情况则保留最短的一条边
}
dijkstra();
if(dist[n]==INF) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << dist[n] << endl;
return 0;
}
CodeTwo:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=15e4+5,INF=999999999;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
//用邻接表去存图
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx;
int w[N];//存权重
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
int n,m;
void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
w[idx]=c;
e[idx]=b;
ne[idx]=h[a];
h[a]=idx++;
}
void dijkstra()
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) dist[i]=INF;
dist[1]=0;
priority_queue<PII,vector<PII>,greater<PII>> heap;//定义小顶堆
heap.push({0,1});//dist[0],first=distance,second=PointLocation
while(heap.size())
{
PII k=heap.top();//取最小距离的点
heap.pop();//弹出
int loc=k.second,dis=k.first;
if(st[loc]) continue;//如果已经找到了最短距离则continue
st[loc]=true;
//常规遍历操作
for (int i = h[loc]; i != -1; i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];//i只是个下标,e中在存的是i这个下标对应的点
if(dist[j]>dis+w[i])
{
dist[j]=dis+w[i];
heap.push({dist[j],j});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);//初始化邻接表
cin >> n >> m ;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c ;
add(a,b,c);
}
dijkstra();
if(dist[n]==INF) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << dist[n] << endl;
}
Experience Get From The Question:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
#include<cstring>
int str[52647];
memset(str,1,sizeof str);//√
memset(str,526471314,sizeof str);//×
//应该逐个赋值
int i=52647-1,j=0;
while(j!=i)
{
cin >> str[j];
j++;
}//√
//对于赋值无穷大(相对),只需
memset(str,0x3f,sizeof str);
Question:AcWing 1375.奶牛回家
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1377
Question Algorithm:dijkstra 最短路
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
直接用 ASCII 码来存储(懒)
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=128;
int g[N][N];
int dist[N];//从Z:90到其他位置的最短长度
int p;
bool st[N];
void dijkstra()
{
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist['Z']=0;
for (int i = 65; i <= 122; i++)//65:A 122:z
{
int t=-1;
for (int j = 65; j <= 122; j++)
{
if(!st[j]&&(t==-1||dist[t]>dist[j])) t=j;
}
st[t]=true;
for (int j = 65; j <= 122; j++)
{
dist[j]=min(dist[j],dist[t]+g[t][j]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
memset(g,0x3f,sizeof g);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) g[i][i]=0;
cin >> p;
for (int i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
char a,b;
int c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
g[(int)a][(int)b]=min(g[(int)a][(int)b],c);
g[(int)b][(int)a]=min(g[(int)a][(int)b],c);
}
dijkstra();
int ans=0x3f3f3f3f,anshome;
for (int i = 'A'; i < 'Z'; i++)//直接遍历有牛的棚,对于不存在的棚也无所谓(因为其dist为INF)
{
if(ans>dist[i])
{
ans=dist[i];
anshome=i;
}
}
cout << char(anshome) << ' ' << ans << endl;
return 0;
Bellman-Ford
一、概念
贝尔曼-福特算法(Bellman-Ford)是由理查德·贝尔曼(Richard Bellman) 和 莱斯特·福特 创立的,求解单源最短路径问题的一种算法。有时候这种算法也被称为 Moore-Bellman-Ford 算法,因为 Edward F. Moore 也为这个算法的发展做出了贡献。它的原理是对图进行 V-1 次松弛操作,得到所有可能的最短路径。其优于迪科斯彻算法的方面是边的权值可以为负数、实现简单,缺点是时间复杂度过高,高达$O(VE)$。但算法可以进行若干种优化,提高了效率。
二、特色
- 求单源最短路径
- 有向图和无向图均可
- 边权可正可负
- 可以解决有边数限制的最短路
三、模板代码
Templated Question:AcWing 853.有边数限制的最短路
Templated Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/855
Templated Question Analysis:
重边就是在两点之间有多条边连接(大于或等于 2)
闭环一条边的起点和终点是一个点
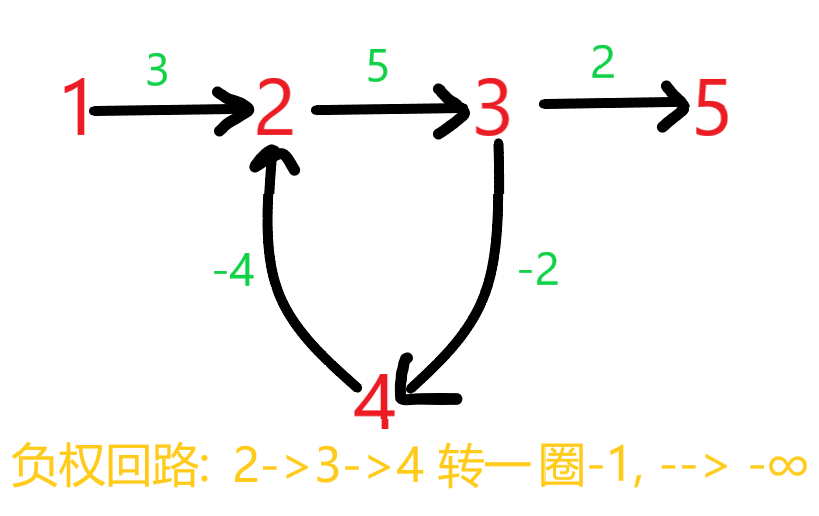
※如果有负权回路,就不一定存在最短路了
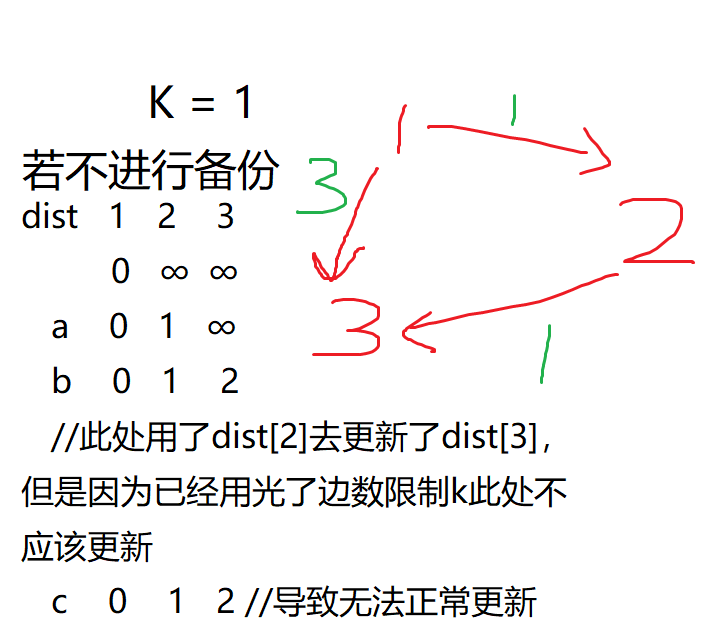
关于备份的解释
Such as:
Templated Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=505,M=10005,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m,k;
int dist[N];
int back[N];//用来备份dist
struct Edge //A Edge a --> b and its value is w
{
int a;
int b;
int w;
}edges[M];
void bellmanford()
{
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);//initialize
dist[1]=0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)//最多经过k条边
{
memcpy(back,dist,sizeof dist);
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)//遍历m条边(所有边)
{
int a=edges[j].a,b=edges[j].b,w=edges[j].w;
dist[b]=min(dist[b],back[a]+w);//以前到a的距离+a->b与到b的距离取小
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x,y,z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
edges[i]={x,y,z};
}
bellmanford();
if(dist[n]>INF/2) puts("impossible");
else cout << dist[n] << endl;
}
FAQ:
Q:Why we need backup array(back[N] in the TemplatedCode)?
A:In case of this condition like:
现在如例图所示,在边数限制为一条的情况下,节点 $3$ 的距离应该为 $3$。
但是由于串联的情况,若不利用备份数组,我们利用 $No.1$ 更新了 $No.2→dist[3]=2$,现在代码中的$dist[b]=min(dist[3]inNo.1,dist[2]inNo.1+w[2→3])=min(∞,2)=2$;
正确的做法是利用 $No.0$ 更新 $No.2→dist[3]=∞$,现在代码中的$dist[b]=min(dist[3]inNo.1$,$dist[2]inNo.0+w[2→3])=min(∞,∞+1)=∞$;
Q:为什么不存在满足要求的路径是 $dist[n]>0x3f3f3f3f/2$ , 而不是 $dist[n]>0x3f3f3f3f$ ?
A:因为程序中的$INF$是一个极大的数,而非真正意义的无穷大,引用上一 Q 的 A,$dist[b]=min(dist[3]inNo.1$,$dist[2]inNo.0+w[2→3])=min(∞,∞+2)=∞$;若$w[2→3]$为负值,那么$dist[b]<0x3f3f3f3f$,不符原意。
$No.0\quad dist[1]=0\quad dist[2]=∞\quad dist[3]=∞$** **
$No.1\quad dist[1]=0\quad dist[2]=1\quad dist[3]=∞$** **
\[No.2\quad dist[1]=0\quad dist[2]=1\quad dist[3]=3\]四、实例代码
SPFA
一、概念
SPFA (Shortest Path Faster Algorithm)算法是** Bellman-Ford**算法的队列优化算法,通常用于求解含负权边的单源最短路径,以及判负环。在最坏情况下,SPFA 算法的时间复杂度和 Bellman-Ford 算法相同,为$O(nm)$;但在稀疏图上运行效率较高,为$O(km)$,其中$k$是一个较小的常数。
二、特色
- 无法计算含有负权回路的最短路径问题
三、模板代码
Templated Question:AcWing 851.spfa 求最短路
Templated Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/853
Templated Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+5;
int n,m;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], w[N], idx;
bool st[N];
int dist[N];
void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
e[idx]=b;
w[idx]=c;
ne[idx]=h[a];
h[a]=idx++;
}
void spfa()
{
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist[1]=0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
st[1]=true;
while(q.size())
{
int bn=q.front();
q.pop();
st[bn]=false;
for (int i = h[bn]; i != -1; i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j]>dist[bn]+w[i])
{
dist[j]=dist[bn]+w[i];
if(!st[j])
{
q.push(j);
st[j]=true;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x,y,z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
add(x,y,z);
}
spfa();
if(dist[n]>0x3f3f3f3f/2) cout << "impossible" << endl;
else cout << dist[n] << endl;
return 0;
}
最短路径问题总结
首先约定 n是点数 m是边数
源点:起点 汇点:终点
二分图
定义
将所有点分成两个集合,使得所有边只出现在集合之间,就是二分图
二分图:一定不含有奇数环,可能包含长度为偶数的环, 不一定是连通图
有两顶点集且图中每条边的的两个顶点分别位于两个顶点集中,每个顶点集中没有边直接相连接!
说人话的定义:图中点通过移动能分成左右两部分,左侧的点只和右侧的点相连,右侧的点只和左侧的点相连。
例如下图左面即为二分图,右面则不是
前缀和
一维前缀和
二维前缀和
首先,我们令某点的值为此点左上角的所有值,用面积的思想来说,即为此点的值为其左上矩形的面积
基于此,可以快速求出任意一个矩形的面积
$S_{Red} = s_{Red} - s_{Green} - s_{Green} + s_{Yellow}$ S 为面积 s 为前缀和。
若 Red_右下(i , j),Red_左上(m, n),那么有
$Res = s[i][j] - s[i - m - 1][j] - s[i][j - n - 1] + s[i - m - 1][j - n - 1]$
与一维前缀和类似,通常会保留第 0 行和第 0 列以防止发生边界问题
如何求出二维前缀和数组呢?
这里以动态规划的思想来求
此处已知绿色(i , j - 1)、蓝色(i - 1, j - 1)、橙色(i - 1, j)矩形面积,欲求红色(i, j)矩形面积,设二维前缀和数组为 $s[N][N]$,那么有
\[s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] + s[i][j - 1] - s[i-1][j - 1]\]Question:AcWing 99. 激光炸弹
Question Link:www.acwing.com/problem/content/101
Question Algorithm:二维前缀和
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5010;
int g[N][N];
int n, r;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> r;
r = min(5005, r);
int maxx = r, maxy = r;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int x, y, w;
cin >> x >> y >> w;
x ++;
y ++;
maxx = max(x,maxx);
maxy = max(y,maxy);
g[x][y] += w;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= maxx; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= maxy; j ++ )
g[i][j] += g[i - 1][j] + g[i][j - 1] - g[i - 1][j - 1];
int res = 0;
for (int i = r; i <= maxx; i ++ )
for (int j = r; j <= maxy; j ++ )
res = max(res, g[i][j] - g[i - r][j] - g[i][j - r] + g[i - r][j - r]);
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
差分
一、概念
于计算机数据结构与算法以侠义理解来说,差分经常运用于数组中前一项 ➖ 后一项 **or 后一项 ➖ 前一项,对差分数组求前缀和**即可得到原数组,例如有
原始数组$int\quad a[]={9,3,6,2,6,8}$
差分数组$int\quad b[]=9$
易知 a 数组是 b 数组的前缀和数组。
我们可以不用考虑差分数组的构造,而是把对于一个区间内的加减操作认为插入原数据来构成差分数组
二、常见问题
- 对于指定区间的每个元素进行加减操作
例如,对数组 a 区间$[left,right]$每个元素加一个常数$c$
只需 $b[left] += c$**, **$b[right+1] −= c$
- 对于用一个数组先存放数据后成为差分数组,需要注意
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
const int N = 52647;
int s[N], n;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cin >> s[i];
//此处需从n向后遍历,避免s[i-1]的意义改变
//此处无需遍历i=1,因为s[1] = s[1] - s[0] = s[1],而s[1]在上个循环已赋值
for(int i = n; i > 1; i ++)
s[i] = s[i] - s[i - 1];
}
- 让整个数组的数变成一样的,只需让除$s[1]$以为的$s[i]$ 均变为 $0$ 即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//因为每次操作会 ?+=C and ? -= C,故可以成对消灭 +-
int pos = 0, neg = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i ++)
{
if(s[i] > 0) pos += s[i];
else neg -= s[i]; //此处存绝对值(正值)
}
三、示例代码
Question:AcWing 101. 最高的牛
Question Link:www.acwing.com/problem/content/103/
Question Algorithm:差分
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5005;
set<pair<int,int>> s;
int n,p,h,m;
int height[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> p >> h >> m;
height[0]=h;
while (m -- )
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
if(a > b) swap(a,b);
if(!s.count({a,b}))
{
s.insert({a,b});
height[a+1]--;height[b]++;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
height[i]+=height[i-1];
cout << height[i] << endl;
}
}
Question:736. 安迪种树
Question Link:www.acwing.com/problem/content/738/
Question Algorithm:前缀和与差分
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+5;
int ans[N];
int n,q;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> q;
while (q -- )
{
int l,r;
cin >> l >> r;
ans[l]++;
ans[r+1]--;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
ans[i]+=ans[i-1];
cout << ans[i] << ' ' ;
}
return 0;
}
Question:AcWing 100. 增减序列
Question Link:www.acwing.com/problem/content/102
Question Algorithm:前缀和与差分
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
typedef long long LL;
int a[N], n;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = n; i > 1; i -- )
a[i] = a[i] - a[i - 1];
LL pos = 0, neg = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if(a[i] > 0) pos += a[i];
else neg -= a[i];
}
cout << min(neg, pos) + abs(neg - pos) << endl;
cout << abs(neg - pos) + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}
四、二维差分数组
插入操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
void insert(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int c)
{
b[x1][y1] += c;
b[x1][y2 + 1] -= c;
b[x2 + 1][y1] -= c;
b[x2 + 1][y2 + 1] += c;
}
回溯操作
1
2
3
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)
b[i][j] += b[i - 1][j] + b[i][j - 1] - b[i - 1][j - 1];
Prim
一、概念
主要用于解决 Minimum Spanning Trees(最小生成树)问题,Prim 算法的基本想法是种一棵树让它从 1 个节点增长到 n 个节点
二、特色
与 Dijkstra 算法有些相似。即先确定一个最小长度的边,用此边长度更新其他边长度,再确定一个最小长度的边,直至遍历了每条边
三、模板代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
const int N=1005,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int g[N][N];// g[i][j] 表示点i和点j之间边的长度
int dist[N];// dist[i] 表示点i到当前集合的最短边的长度
//@@注意,此处dist与dijkstra算法中的dist不同@@
bool st[N];// st[i] 表示点i是否在当前生成树集合中
int n;//端点数
int prim()
{
//init
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) dist[i]=INF;
memset(st,false,sizeof st);
int res=0;
dist[1]=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int t=-1;//当前最短的边的序号
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)//寻找当前最短的边序号
if(!st[j]&&(t==-1||dist[t]>dist[j])) t=j;
st[t]=true;//dist[t]已确定
res+=dist[t];
//用新加入的点(t)更新其余点到生成树的最短边
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if(!st[j]) dist[j]=min(dist[j],g[t][j]);
}
return res;
}
四、示例代码
Question:LaoQiao C/C++ Group B 2020.4 9.通电
Question Link:blog.csdn.net/Cyril_KI/article/details/108369516
Question Algorithm:Minimum Spanning Trees
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=1005,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
double g[N][N];// g[i][j] 表示点i和点j之间边的长度
double dist[N];// dist[i] 表示点i到当前集合的最短边的长度
bool st[N];// st[i] 表示点i是否在当前生成树集合中
int n;
struct Loc
{
int x;
int y;
int h;
}loc[N];
double cal(Loc a,Loc b)
{
return (double)sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y))+(a.h-b.h)*(a.h-b.h);
}
double prim()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) dist[i]=INF;
memset(st,false,sizeof st);
double res=0;
dist[1]=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int t=-1;//当前最短的边
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)//寻找当前最短的边
if(!st[j]&&(t==-1||dist[t]>dist[j])) t=j;
st[t]=true;//dist[t]已确定
res+=dist[t];
//用新加入的点(t)更新其余点到生成树的最短边
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if(!st[j]) dist[j]=min(dist[j],g[t][j]);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
memset(g,0x3f,sizeof g);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> loc[i].x >> loc[i].y >> loc[i].h;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = i; j <= n; j++)//令j=i可以略微减少运算
g[i][j]=g[j][i]= i==j ? 0 : cal(loc[i],loc[j]);
cout << prim() << endl;
return 0;
}
Kruskal
一、概念
主要用于解决 Minimum Spanning Trees(最小生成树)问题。
Kruskal 算法的主要思想是 先选择权值较小的边,检查是否存在回路,然后继续选择,直到选择了 n-1 (顶点数-1) 的边 结束。
在检查回路时,通常运用并查集。
二、模板代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
const int N=1005;//Nodes Count
const int M=2010;//Edges Count
int p[N];//p[i]记录节点 i 的父节点
int n;//顶点数
int res=0;
struct Edge
{
int a;//Start Point of the edge
int b;//End Point of the edge
int v;//The Value of the edge
}edge[M];
int find(int x)
{
return p[x]==x ? x : p[x]=find(p[x]);
/*
if(p[x]==x)//如果其父节点是其本身(它就是最nb的节点)
return x;
else
p[x]=find(p[x]);//令x的父节点p[x]去寻找其父节点并赋值(路径压缩)
return find(p[x]);
*/
}
void merge(int x,int y)
{
p[find(x)]=find(y);
}
bool cmp(Edge x,Edge y)
{
return x.v<y.v;
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i]=i;//初始每个节点的父节点都为自己
//Input every edges info
/* Code */
sort(edge,edge+idx,cmp);//idx:边数
int cnt=0;//记录已选择边的数量
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i++)//枚举选择每条边
{
int x=edge[i].a,y=edge[i].b;
if(find(x)!=find(y)) //没有成环
{
cnt++;
merge(x,y);
res+=edge[i].v;
if(cnt==n-1) break;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
三、示例代码
Question:LaoQiao C/C++ Group B 2020.4 9.通电
Question Link:blog.csdn.net/Cyril_KI/article/details/108369516
Question Algorithm:Minimum Spanning Trees
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N=1005,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int p[N];//p[i]记录节点 i 的父节点
int n;
double res=0.0;
struct Loc
{
int x;
int y;
int h;
}loc[N];
struct Edges
{
int a;//Start Point
int b;//End Point
double v;//The Value of the edges
}edge[N];
double cal(Loc a,Loc b)
{
return (double)sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y))+(a.h-b.h)*(a.h-b.h);
}
bool cmp(Edges x,Edges y)
{
return x.v<y.v;
}
int find(int x)
{
return p[x]==x ? x : p[x]=find(p[x]);
}
void merge(int x,int y)
{
p[find(x)]=find(y);
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i]=i;
int idx=0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> loc[i].x >> loc[i].y >> loc[i].h;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if(i==j) continue;
edge[idx].a=i;
edge[idx].b=j;
edge[idx].v=cal(loc[i],loc[j]);
idx++;
}
sort(edge,edge+idx,cmp);
int cnt=0;//记录已选择边的数量
//在不形成环的条件下依次选择n - 1条边,并把它们的权值相加输出
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i++)
{
int x=edge[i].a,y=edge[i].b;
if(find(x)!=find(y)) //没有成环
{
cnt++;
merge(x,y);
res+=edge[i].v;
if(cnt==n-1) break;
}
}
printf("%.2f",res);
return 0;
}
最小生成树问题总结
哈夫曼树及求其 WPL 算法
一、概念
给定$N$个权值作为 $N$个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树 ,若该树的带权路径长度达到最小 ,称这样的二叉树 为最优二叉树 ,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree) 。哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。
霍夫曼树与哈夫曼树是一样的,只是音译的问题。
二、相关知识
1、路径和路径长度
在一棵树中,从一个结点往下可以达到的孩子或孙子结点之间的通路,称为路径。通路中分支的数目称为路径长度。若规定根结点的层数为 1,则从根结点到第 $L$ 层结点的路径长度为 $L−1$。
2、结点的权及带权路径长度
若将树中结点赋给一个有着某种含义的数值,则这个数值称为该结点的权。结点的带权路径长度为:从根结点到该结点之间的路径长度与该结点的权的乘积。
3、树的带权路径长度
树的带权路径长度规定为所有叶子结点的带权路径长度之和,记为 $WPL$。
三、如何构造哈夫曼树?
凭直觉 (反正我是这样想的) 肯定要把权值大的点 放在树的最上层 ,因为这样才能使得该叶节点的带权路径长度 最小,但与此同时,这个点就不能够再有孩子了(因为他是叶节点),不能有孩子,那么就要增加深度 ,深度 又和带权路径长度 相关,所有这时候就要用到霍夫曼算法
霍夫曼算法
- 初始化:由给定的$N$个权值构造$N$棵只有一个根节点的二叉树,得到一个二叉树集合$F$。
- 选取与合并:从二叉树集合$F$中选取根节点权值 最小的两棵 二叉树分别作为左右子树构造一棵新的二叉树,这棵新二叉树的根节点的权值为其左、右子树根结点的权值和。
- 删除与加入:从$F$中删除作为左、右子树的两棵二叉树,并将新建立的二叉树加入到 中。
- 重复 2、3 步,当集合$F$中只剩下一棵二叉树时,这棵二叉树就是霍夫曼树。
若只求$WPL$,可用小根堆来模拟,此用[一道例题]来说明
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1005;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> q;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
int temp;
cin >> temp;
q.push(temp);
}
int res = 0;
while(q.size() > 1)
{
int x = q.top();
q.pop();
int y = q.top();
q.pop();
q.push(x + y);
res += x + y;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
题中实例数据($1\quad2\quad 2\quad 5 \quad9$ 为权值)作为样例图示:
哈夫曼树知识点比较独立,故记于此。
Reference: [哈夫曼树(赫夫曼树、最优树)详解] [霍夫曼树 OI Wiki] [AcWing 3531.哈夫曼树 WanJY 的题解]
LCA 最近公共祖先
一、概念
对于有根树$T$的两个结点$u、v$,最近公共祖先$LCA(T,u,v)$表示一个结点$x$,满足$x$是$u$和$v$的祖先且$x$的深度尽可能大。在这里,一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先。
如图所示,$A$与$B$的最近公共祖先是$C$
二、算法
二叉树暴力法
由例题得此方法,可能会因条件特殊而不可使用
思路
先让两点的深度一样然后逐级向上遍历即可,遍历到的第一个相同的点即为最近公共祖先
仅适用于紧挨着点的距离为 1 的情况!
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
//这里,令dist[i]表示 i 距离 根结点root 的距离
//令p[i]表示为 i 的父节点
//且dist[x] > dist[y]
int get_lca(int x, int y)// dist[x] > dist[y]
{
if(dist[x] < dist[y]) return get_lca(y, x);
//让两点的深度一样
while (dist[x] > dist[y]) x = p[x];//对于节点之间距离相同的情况,长度相同则深度相同
//向上遍历
while (x != y) x = p[x], y = p[y];
return x;
}
例题
Question:AcWing 3555.二叉树
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/3558
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
对于树上两个结点的最短路径长度,最简单暴力的是存成图,用最短路径算法,但由于是在树上,且父节点与子节点的距离是一,所以此题可转换为 LCA 问题
若求节点$A$与节点$B$之间的最短路径长度,则为$dist[A] + dist[B] - 2 × dist[C]$
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int l[N], r[N], p[N], dist[N];
void dfs(int u, int d)
{
if(l[u] != -1) dfs(l[u], d + 1);
if(r[u] != -1) dfs(r[u], d + 1);
dist[u] = d;
}
int get_lca(int x, int y)// dist[x] > dist[y]
{
if(dist[x] < dist[y]) return get_lca(y, x);
while (dist[x] > dist[y]) x = p[x];//长度相同则深度相同
while (x != y) x = p[x], y = p[y];
return x;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T -- )
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
l[i] = a, r[i] = b;
if(a != -1) p[a] = i;
if(b != -1) p[b] = i;
}
dfs(1,0);
while (m -- )
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
int z = get_lca(x, y);
cout << dist[x] + dist[y] - 2 * dist[z] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
向上标记法
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
现有两点$x,y$,树根为$u$,标记$x\to u$经过的所有点,然后在$y\to u$过程中遇到的第一个标记的点就是两者的 LCA
倍增
时间复杂度:$O(n\log(n))$
步骤:
- 预处理$fa[i][j]$表示从$i$开始,向上走 $2^j$步所能走到的节点,其中$0 \leq j \leq \log(n)$。预处理$depth[i]$表示深度。$O(n\log(n))$
哨兵:如果从$i$开始跳 $2^j$步会跳过根节点,那么$fa[i][j] = 0, dist[0] = 0$
- 先将两个点跳到同一层。$O(\log(n))$
- 让两个点同时往上跳,直到一直跳到它们的 LCA 的下一层(上一层(fa[k][0])就是它们的 LCA)。$O(\log(n))$
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
const int N = 40010, M = 2 * N; // N 为点数, M 为边数
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx; // 邻接表
int n, m, depth[N], fa[N][16]; // log2(40000) = 15.2877
void bfs(int root) // 预处理depth,fa
{
memset(depth, 0x3f, sizeof depth);
depth[0] = 0; // 哨兵
depth[root] = 1;
queue<int> q;
q.push(root);
while (q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(depth[j] > depth[t] + 1)
{
depth[j] = depth[t] + 1;
q.push(j);
fa[j][0] = t;
for (int k = 1; k <= 15; k ++ )
fa[j][k] = fa[fa[j][k - 1]][k - 1];
// j -> 2^k == j -> 2^{k-1} -> 2^{k-1}
// 2^{k-1} + 2^{k-1} = 2^k
}
}
}
}
int lca(int a, int b)
{
if(depth[a] < depth[b]) swap(a, b);
for (int k = 15; k >= 0; k --)
if(depth[fa[a][k]] >= depth[b])
a = fa[a][k];
if(a == b) return a;
for (int k = 15; k >= 0; k --)
if (fa[a][k] != fa[b][k])
{
a = fa[a][k];
b = fa[b][k];
}
return fa[a][0]; // 跳到它们的LCA的**下一层**
}
例题
Question:AcWing 1172.祖孙询问
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/1174
Question Difficulty Level:★★☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 40010, M = 2 * N;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int n, m, depth[N], fa[N][16]; // log2(40000) = 15.2877
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx ++;
}
void bfs(int root)
{
memset(depth, 0x3f, sizeof depth);
depth[0] = 0, depth[root] = 1;
queue<int> q;
q.push(root);
while (q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(depth[j] > depth[t] + 1)
{
depth[j] = depth[t] + 1;
q.push(j);
fa[j][0] = t;
for (int k = 1; k <= 15; k ++ )
fa[j][k] = fa[fa[j][k - 1]][k - 1];
}
}
}
}
int lca(int a, int b)
{
if(depth[a] < depth[b]) swap(a, b);
for (int k = 15; k >= 0; k --)
if(depth[fa[a][k]] >= depth[b])
a = fa[a][k];
if(a == b) return a;
for (int k = 15; k >= 0; k --)
if (fa[a][k] != fa[b][k])
{
a = fa[a][k];
b = fa[b][k];
}
return fa[a][0];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
int root = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if(b == -1) root = a;
else add(a, b), add(b, a);
}
bfs(root);
cin >> m;
while (m -- )
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int p = lca(a, b);
if(p == a) cout << 1 << endl;
else if(p == b)cout << 2 << endl;
else cout << 0 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Tarjan
时间复杂度:$O(n+m)$
思路:
在深度优先遍历的时,将所有点分成三大类
- 已经遍历过,且回溯过的点 2
- 正在搜索的分支 1
- 还未搜索到的点 0
DFS 深度优先遍历
一、概念
一条路走到黑,黑了再回头,回头再走到黑
Question:AcWing 3428.放苹果
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/3431
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
- 数据规模不大,无需$dp$,用$dfs$即可
- 因为每个苹果和盘子都是相同的,所以为防止重复,指定一个顺序为从小到大,用$last$记录上一次选择的数字
- 本题$dfs函数$比较特殊(?也可能见得少)。前面的$if$为$res$服务
- \[u:表示第 u 个盘子\]
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
int dfs(int u, int sum, int last)
{
if(u == n)
{
if(sum == 0) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = last; i <= sum; i ++ )
res += dfs(u + 1, sum - i, i);
return res;
}
int main()
{
while (cin >> m >> n)
cout << dfs(0, m, 0) << endl;
return 0;
}
双指针
一、概念
二、时间复杂度$O(n)$
三、适用条件
两个指针互相单调。
例如,随着$r指针$向右/左移动,$l指针$必向左或右移动。
四、实例代码
Question:4405. 统计子矩阵 第十三届蓝桥杯省赛 C++B 组第六题
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/4408
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
暴力是四维,需要优化一维。
先限定上限和下限,左右限制可以通过$k$来得出
对于二分$O(nlogn)$有点悬,故选用双指针$O(n)$
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510;
int s[N][N];
int n, m, k;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
{
cin >> s[i][j];
s[i][j] += s[i - 1][j];
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = i; j <= n; j ++ )
{
for (int l = 1, r = 1, sum = 0; r <= m; r ++)
{
sum += s[j][r] - s[i - 1][r];
while (sum > k)
{
sum -= s[j][l] - s[i - 1][l];
l ++;
}
res += r - l + 1;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
0-1 最短路问题
适用算法:双端队列 BFS(实际就是 Dijkstra 算法)
数论
试除法判断质数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
bool isprime(int x)
{
if(x < 2) return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
if(x % i == 0) return false;
return true;
}
试除法分解质因数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
void divide(int x)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
{
int cnt = 0;
while(x % i == 0) cnt ++, x /= i;
if(cnt) cout << i << ' ' << cnt << endl;
}
if(x > 1) cout << x << ' ' << 1 << endl;
cout << endl;
}
埃氏筛
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
int primes[N], cnt;
bool st[N];
void getprimes(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n ; i ++ )
{
if(!st[i]) // i is prime
{
primes[cnt ++] = i;
for (int j = i + i; j <= n; j += i)
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
约数个数
详情见约数之和分析过程,此处给出一个定理:
\[(\prod_{i=1}^{n} a[i])的质因数 = \prod_{i=1}^{n}(a[i]的质因数)\]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
//Question Link:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/872/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int Mod = 1e9+7;
unordered_map<int, int> cnt;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
{
int s = 0;
while(x % i == 0) s ++, x /= i;
cnt[i] += s;
}
if(x > 1) cnt[x] ++;
}
long long res = 1;
for(auto [key, val] : cnt)
res = res * (1 + val) % Mod;
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
约数之和
具体定理及定义请看百度百科,此处只给出结论和部分推导
思路
对于一个大于 1 的正整数$n$可以分解质因数
$n = p_1^{k1}×p_2^{k2}×…×p_n^{kn}$
经分析可知在一对$(pn,kn)$中进行选择则可得出一个因数,且不同的选择因数是不同的
易得$n$的正约数个数为
$(p_1+1)×(p_2+1)×…×(p_n+1)$个(因为有 $0$ 次方所以需要$+1$)
进而易得约数之和为 (it’s not easy to know qwq)
\[(p_1^0+p_1^1+...+p_1^{k_1})×(p_2^0+p_2^1+...+p_2^{k_2})×...×(p_n^0+p_n^1+...+p_n^{k_n})\]此处用选择的思想比较容易理解
辅助函数
此处再给出一个函数$sum(p, k) = p^0+p^1+…+p^k$
通过分治算法写出递归函数降低时间复杂度
数学分析过程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
/*
* sum(p, k) = p^0+p^1+...+p^k
* if k is odd and k + 1 is even
* = p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2) + p^(k/2+1)+p^(k/2+2)+p^n Notice A k is odd 仅保留整数
* = p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2) + p^(k/2+1)*(p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2)) Notice Because of Notice A k/2 + k/2 + 1 = k
* = (1 + p^(k/2+1)) * (p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2))
* = (1 + p^(k/2+1)) * sum(p, k / 2)
* if k is even and k + 1 is odd
* = p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2) + p^(k/2+1)+p^(k/2+2)+p^n
* = sum(p, k - 1) * p + 1 Notice 1 = p^0
*/
//《关于受不了再改Latex所以直接cv这档子事》
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//此处qmi为快速幂函数,Mod为模
int sum(int p, int k)
{
if(!k) return 1;
if(k % 2) return sum(p, k / 2) % Mod * (1 + qmi(p, k / 2 + 1)) % Mod;//k is odd but k + 1 is even
else return (p % Mod * sum(p, k - 1) % Mod + 1) % Mod;//k is even but k + 1 is odd
}
例题
Question:AcWing 97. 约数之和
Question Link:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/99/
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
最后直接$×B$即可
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
/**
* A分解质因数 A = p1^k1 * p2^k2 * ... * pn^kn
* 那么A的正约数个数即为在每个(p,n)中选择(0 ~ n)个p进行相乘的数目
* 即在 pn^kn中选(0,kn)个pn n 属于(0,n)
* 依此方法选择的约数不重不漏
* A的正约数的个数即为(p1+1)*(p2+1)*...*(pn+1)个(因为有0次方所以需要+1)
* A的正约数的和即为(p1^0+p1^1+...+p1^k1)*(p2^0+p2^1+...+p2^k2)*...*(pn^0+pn^1+...+pn^kn)
* (用选择的思想可以比较容易理解)
* 我们只需要一个函数sum(p ,k) 去计算 (p^0+p^1+...+p^k) 即可
* sum(p, k) = p^0+p^1+...+p^k
* if k is odd and k + 1 is even
* = p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2) + p^(k/2+1)+p^(k/2+2)+p^n Notice A k is odd 仅保留整数
* = p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2) + p^(k/2+1)*(p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2)) Notice Because of Notice A k/2 + k/2 + 1 = k
* = (1 + p^(k/2+1)) * (p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2))
* = (1 + p^(k/2+1)) * sum(p, k / 2)
* if k is even and k + 1 is odd
* = p^0+p^1+...+p^(k/2) + p^(k/2+1)+p^(k/2+2)+p^n
* = sum(p, k - 1) * p + 1 Notice 1 = p^0
*
*
* p * sum(p, k - 1)+ 1
*
*
* %Mod的位置太考究了,建议直接使用long long
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int Mod = 9901;
int qmi(int a, int k)
{
a %= Mod;
int res = 1;
while (k)
{
if (k & 1) res = res * a % Mod;
a = a * a % Mod;
k >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int sum(int p, int k)
{
if(!k) return 1;
if(k % 2) return sum(p, k / 2) % Mod * (1 + qmi(p, k / 2 + 1)) % Mod;//k is odd but k + 1 is even
else return (p % Mod * sum(p, k - 1) % Mod + 1) % Mod;//k is even but k + 1 is odd
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int res = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= a; i ++ )
{
int cnt = 0;
while(!(a % i))
{
cnt ++;
a /= i;
}
if(cnt) res = res * sum(i, cnt * b) % Mod;
}
if(!a) res = 0;
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
欧拉函数
在数论中,对正整数 n,欧拉函数是小于 n 的正整数中与 n 互质的数的数目。
首先将正整数$n$分解质因数$n = p_1^{k1}×p_2^{k2}×…×p_n^{kn}$ ,那么欧拉函数公式为
\[φ(n) = n(1-\frac1{p_1})(1-\frac1{p_2})...(1-\frac1{p_n})\]具体证明过程略,其中运用了容斥原理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
//Question Link: https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/875/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n -- )
{
int a;
cin >> a;
int res = a;
for (int i = 2; i <= a / i; i ++ )
{
if(a % i == 0) res = res / i * (i - 1);
while(a % i == 0) a /= i;
}
if(a > 1) res = res / a *(a - 1);
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
筛法求欧拉函数
欧拉定理
若$a$与$n$互质,则$a^{φ(n)} mod n = 1 $恒成立
组合数
递推公式求组合数
\[C_a^b = C_{a-1}^b + C_{a-1}^{b-1} \]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2010, Mod = 1e9 + 7;
int c[N][N];
void init()
{
for(int i = 0; i < N; i ++)
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j ++)
if(!j) c[i][j] = 1;
else c[i][j] = (c[i - 1][j] + c[i - 1][j - 1]) % Mod;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
init();
while (n -- )
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << c[a][b] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
预处理阶乘求组合数
\[C_a^b = \frac{a!}{b!(a-b)!}\] \[∵\frac{a! \% Mod}{b!(a-b)! \% Mod} ≠ \frac{a!}{b!(a-b)!} \% Mod\]$∴C_a^b = \frac{a!}{b!(a-b)!} = a!{b!}^{-1}{(a-b)!}^{-1}\%Mod$ 费马小定理求逆元(Mod 是质数)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, Mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef long long LL;
int fact[N], infact[N];
int qmi(int a, int k, int p)
{
int res = 1;
while(k)
{
if(k & 1) res = (LL)res * a % p;
a = (LL)a * a % p;
k >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void init()
{
fact[0] = infact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i ++ )
{
fact[i] = (LL)fact[i - 1] * i % Mod;
infact[i] = (LL)infact[i - 1] * qmi(i, Mod - 2, Mod) % Mod;
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
init();
while (n -- )
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << (LL)fact[a] * infact[b] % Mod * infact[a-b] % Mod << endl;
}
return 0;
}
卢卡斯定理求组合数
\[C_{a}^b ≡ C_{a\%p}^{b\%p} C_{a/p}^{b/p} (mod p)\]Hash
字符串哈希
字符串哈希顾名思义则是将字符串映射成数字。
这里,通常把一个字符先映射为一个数字,此处拿均为小写字母的字符串为例,a代表1 b代表2 …,那么对于字符串 abc 则等价于 $123_{P}$ (123 的 P 进制)以此来进行 Hash。
通常取 P = 131 or 13331 ,但要注意,必须满足字符种数 > P。
在 C++ 中,无需对 P进制数 结果求模,通常采用 unsigned long long 溢出自动求模。(unsigned long long max = $2^{64}-1$)
总结:P = 131 or 13331, 在 $2^{64}-1 $ 范围内的数字映射
快速求出字符串子串的 Hash 值
首先定义前缀哈希数组 h[N]:h[i]表示子串(1, i)的Hash值
接上例,若现有一字符串 s="abc" 转化成数字即为 123, P = 131,那么则有
$h[2] = 1P^1 + 2P^0 = 133$
\[h[3] = 1*P^2+2*P^1+3*P^0 = 17476\]易得已知 $h[i - 1] $ 则有 $h[i] = h[i - 1] * P + (s[i] - ’a’ + 1) $
*P 使得所有位提高一位
(s[i] - 'a' + 1) 加上新字符所对应的数
根据以上可得出求得字符串(StartIdx,EndIdx)的子串的 Hash 即为$hash = h[EndIdx] - h[StartIdx - 1] × P^{EndIdx - StartIdx + 1}$
我们可以先预处理出 $P^{ 字符串个数次方}$ 的数组来降低出字符串子串的 Hash 值的时间复杂度
Question:AcWing 138.兔子与兔子
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/140
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
字符串 Hash
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010, base = 131;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
ULL h[N],p[N];
ULL get(int l, int r)
{
return h[r] - h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1];
}
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
s = ' ' + s;
h[0] = 0;
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= s.size(); i ++ )
{
h[i] = h[i - 1] * base + (s[i] - 'a' + 1);
p[i] = p[i - 1] * base;
}
int m;
cin >> m;
while (m -- )
{
int l1, r1, l2, r2;
cin >> l1 >> r1 >> l2 >> r2;
if(get(l1, r1) == get(l2, r2)) cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
}
}
欧几里得距离 Hash
Question:AcWing 1402.星空之夜
Question Link: 1402. 星空之夜 - AcWing 题库
Question Difficulty Level:★★☆☆☆ Novelty but can be dealt by BF
Question Analysis:
对星群进行 Hash,需要找到对于如下八种情况,Hash 相同的 Hash 函数
可见,每个星群内部每对点($C_n^2$)的欧几里得距离之和可以作为唯一 key
注意:double 之间的相等比较
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 110;
const double eps = 1e-8;
char g[N][N];
int n, m;
int dx[8] = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0};
int dy[8] = {-1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1};
vector<PII> loc;
vector<double> hashList;
void dfs(int x, int y){
g[x][y] = '0';
loc.push_back({x, y});
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i ++ ){
int tx = x + dx[i], ty = y + dy[i];
if (tx >= 0 && tx < n && ty >= 0 && ty < m && g[tx][ty] == '1') dfs(tx, ty);
}
}
double get_dist(PII& a, PII& b){ // 传引用可以加快速度
// return sqrt((double)abs(a.first - b.first) + abs(a.second - b.second)); type convert error
double dx = a.first - b.first, dy = a.second - b.second;
return sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
double get_hash(){
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < loc.size(); i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++ )
sum += get_dist(loc[i], loc[j]);
return sum;
}
char get_id(){
double hash = get_hash();
for (int i = 0; i < hashList.size(); i ++ )
if (abs(hashList[i] - hash) <= eps){ // if find hash loc
return 'a' + i;
}
hashList.push_back(hash);
return 'a' + hashList.size() - 1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> g[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++ ){
if (g[i][j] == '1'){
loc.clear();
dfs(i, j);
char id = get_id();
for (auto [x, y] : loc) g[x][y] = id;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cout << g[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
树的遍历
遍历树中的所有点,路径中可以包含重复的点和边
经分析可知,答案为所有边长度 ×2-起点到终点的距离
Question:AcWing 4706. 最短路程
Question Link:acwing.com/problem/content/4709
Question Difficulty Level:★☆☆☆☆
Question Analysis:
思维题 树的遍历
Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 2 * N;
typedef long long LL;
int n;
int h[N], e[M], w[M], ne[M], idx;
void add(int a, int b, int c) // 添加一条边a->b,边权为c
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int dfs(int u, int fa)
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(j == fa) continue;
res = max(res, dfs(j, u) + w[i]);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
LL sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ )
{
int x, y, z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
add(x, y, z);
add(y, x, z);
sum += 2 * z;
}
cout << sum - dfs(1, -1) << endl;
return 0;
}
树的直径
一、概念
树的直径是指树上最远的两个节点之间的距离,也被称为树的最长链。
二、求法
DFS
Step:
- 任取一点
x进行 DFS,记录其他点到x的距离dist[] - 找
dist[]数组最大值dist[u](u为树的直径的端点),对dist[u]进行 DFS,更新dist[]数组 dist[]数组里最大值即为树的直径
Provement: 主要证明 u 为树的直径的端点
树形 DP
Sort in C++
sort
sort 是基于快排实现的,是一种不稳排序。
理想情况下时间复杂度 $O(NlogN)$,空间复杂度$O(logN)$,极端情况下时间复杂度$O(N^2)$,空间复杂度$O(N)$
stable_sort
stable_sort 是基于归并排序的,是一种稳定排序。
时间复杂度$O(NlogN)$,空间复杂度$O(N)$
stable_sort(first,last,cmp)
stable_sort 对 cmp函数 的调用次数较少,例题如下
快速排序
排序等知识并不常考,此处仅记录思路与模板
思路
运用分治及递归的思想,每次选取一个区间,对这个区间中选取一个值,然后通过一系列操作使得该区间分成两个区间一个区间大于所选取的值,另一个区间小于所选取的值,然后递归处理两个区间,当所处理区间不合法时结束递归。
一系列操作:这里仅给出一种比较优雅的写法,我们定义两个指针$i,j$,其中$i=l-1$ $j = r + 1$
具体为何
l - 1 r + 1请看 y 总视频讲解才不是因为忘了
每次先令$i++$ $j –$ 然后进行 while 判断,while 结束后,若指针合法则交换两个指针所指内容
模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
void quick_sort(int l, int r)
{
if(l >= r) return;
int i = l - 1, j = r + 1, val = w[l + r >> 1];
while(i < j)
{
do i ++;while(w[i] < val);
do j --;while(w[j] > val);
if(i < j) swap(w[i], w[j]);
}
quick_sort(l, j);
quick_sort(j + 1, r);
}
归并排序
排序等知识并不常考,此处仅记录思路与模板
思想
运用分治及递归的思想,每次先将区间一分为二进行递归,然后进行归并操作。
首先有区间$[l, mid],[mid+1,r]$,设$i = l, j= (l + r) / 2 + 1$,由于递归,经分析可知这两区间均为单调,故进行归并操作,同时比较归并至一个临时数组同时移动两个指针知道某个指针结束,然后将未被归并进的数按原序存入临时数组,然后将临时数组覆盖在原数组的$[l,r]$
模板
1
容斥原理
简单博弈论
NIM 游戏
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
给定N堆物品,第i堆物品有Ai个。两名玩家轮流行动,每次可以任选一堆,取走任意多个物品,可把一堆取光,但不能不取。取走最后一件物品者获胜。两人都采取最优策略,问先手是否必胜。
我们把这种游戏称为NIM博弈。把游戏过程中面临的状态称为局面。整局游戏第一个行动的称为先手,第二个行动的称为后手。若在某一局面下无论采取何种行动,都会输掉游戏,则称该局面必败。
所谓采取最优策略是指,若在某一局面下存在某种行动,使得行动后对面面临必败局面,则优先采取该行动。同时,这样的局面被称为必胜。我们讨论的博弈问题一般都只考虑理想情况,即两人均无失误,都采取最优策略行动时游戏的结果。
NIM博弈不存在平局,只有先手必胜和先手必败两种情况。
定理: NIM博弈先手必胜,当且仅当 A1 ^ A2 ^ ... ^ An != 0
公平组合游戏 ICG
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
若一个游戏满足:
1. 由两名玩家交替行动;
2. 在游戏进程的任意时刻,可以执行的合法行动与轮到哪名玩家无关;
3. 不能行动的玩家判负;
则称该游戏为一个公平组合游戏。
NIM博弈属于公平组合游戏,但城建的棋类游戏,比如围棋,就不是公平组合游戏。因为围棋交战双方分别只能落黑子和白子,胜负判定也比较复杂,不满足条件2和条件3。
有向图游戏
1
2
3
给定一个有向无环图,图中有一个唯一的起点,在起点上放有一枚棋子。两名玩家交替地把这枚棋子沿有向边进行移动,每次可以移动一步,无法移动者判负。该游戏被称为有向图游戏。
任何一个公平组合游戏都可以转化为有向图游戏。具体方法是,把每个局面看成图中的一个节点,并且从每个局面向沿着合法行动能够到达的下一个局面连有向边。
Mex 运算
1
2
3
设S表示一个非负整数集合。定义mex(S)为求出不属于集合S的最小非负整数的运算,即:
mex(S) = min{x}, x属于自然数,且x不属于S
SG 函数
1
2
3
4
5
在有向图游戏中,对于每个节点x,设从x出发共有k条有向边,分别到达节点y1, y2, ..., yk,定义SG(x)为x的后继节点y1, y2, ..., yk 的SG函数值构成的集合再执行mex(S)运算的结果,即:
SG(x) = mex({SG(y1), SG(y2), ..., SG(yk)})
特别地,整个有向图游戏G的SG函数值被定义为有向图游戏起点s的SG函数值,即SG(G) = SG(s)。
有向图游戏的和
1
2
3
4
5
设G1, G2, ..., Gm 是m个有向图游戏。定义有向图游戏G,它的行动规则是任选某个有向图游戏Gi,并在Gi上行动一步。G被称为有向图游戏G1, G2, ..., Gm的和。
有向图游戏的和的SG函数值等于它包含的各个子游戏SG函数值的异或和,即:
SG(G) = SG(G1) ^ SG(G2) ^ ... ^ SG(Gm)
定理
1
2
3
有向图游戏的某个局面必胜,当且仅当该局面对应节点的SG函数值大于0。
有向图游戏的某个局面必败,当且仅当该局面对应节点的SG函数值等于0。
MathKnowledge
排序不等式(Rearrangement Inequality)
内容
设有两数列$a_1,a_2,\cdots,a_n$和$b_1,b_2,\cdots,b_n$,满足$a_1 \leq a_2 \leq \cdots \leq a_n$,$b_1 \leq b_2 \leq \cdots \leq b_n$,$c_1,c_2,\cdots,c_n$是$b_1,b_2,\cdots,b_n$的乱序排列,则有
\[\sum_{i=1}^{n}a_i b_{n+1-i} \leq \sum_{i=1}^{n}a_i c_i\leq \sum_{i=1}^{n}a_i b_i\]当且仅当$a_i=a_j$或$b_i=b_j\ (1\leq i, j \leq n)$时等号成立
分拆数
分拆:将自然数 $n$ 写成递降正整数和的表示。
\[n=r_1+r_2+\ldots+r_k \quad r_1 \ge r_2 \ge \ldots \ge r_k \ge 1\]和式中每个正整数称为一个部分。
分拆数:$p_n$。自然数 $n$ 的分拆方法数。
k 部分拆数
将 $n$ 分成恰有 $k$ 个部分的分拆,称为 $k$ 部分拆数,记作 $p(n,k)$。
显然,$k$ 部分拆数 $p(n,k)$ 同时也是下面方程的解数:
\[n-k=y_1+y_2+\ldots+y_k\quad y_1\ge y_2\ge\ldots\ge y_k\ge 0\]如果这个方程里面恰有 $j$ 个部分非 $0$,则恰有 $p(n-k,j)$ 个解。因此有和式:
\[p(n,k)=\sum_{j=1}^k p(n-k,j)\]相邻两个和式作差,得:
\[p(n,k)=p(n-1,k-1)+p(n-k,k)\]Some Typical Problem
合法括号序列
合法括号序列可以被等价地描述为
- 序列中左括号与右括号数量相等
- 序列的任意前缀中,左括号数量$\geq$右括号数量
- 通常用栈实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
bool check(string s){
stack<char> stk;
for (char c : s){
if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{') stk.push(c);
else {
if (stk.empty()) return false;
if (stk.top() == '(' && c != ')') return false;
if (stk.top() == '[' && c != ']') return false;
if (stk.top() == '{' && c != '}') return false;
stk.pop();
}
}
return stk.empty();
}
int main(){
if (check("[([][])]")) cout << "is legall" << endl;
return 0;
}
区间最值问题
区间最值问题在一个连续的区间上的最大\小值问题,有多种实现方法
By Multiset
Stern-Brocot Tree
定义
Stern-Brocot Tree 是一种人为构造生成 所有正有理数的树形结构,树上的每个节点与全体有理数(最简形式) 构成双射。
More detail in Stern-Brocot Tree - Achtoria - 博客园
Queston AcWing 1360. 有序分数
Question Link:1360. 有序分数 - AcWing 题库
###
离散化
定义
离散化,把无限空间中有限的个体映射到有限的空间中去,以此提高算法的时空效率。
通俗的说,离散化是在不改变数据相对大小的条件下,对数据进行相应的缩小。
实现
二分方法实现
将原数据打包进数组进行排序,用二分来查找某原数据的下标,即为该原数据的离散值(相对大小位置)
Question: AcWing 802. 区间和
Question Link: 802. 区间和 - AcWing 题库
The key Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
int turn(int loc)
{
int l = 0, r = idx.size() - 1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(idx[mid] >= loc) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r + 1;//所有值加1为了前缀和数组
}
std::map<originalValue, discretizationValue> 实现
将原数据打包进数组进行排序,用 map 来存储,其中 key 为原值,val 为离散化后的值
The key Code:
1
2
3
4
unordered_map<int, int> h;
int idx = 1;
sort(...);
for (int x : location) h[x] = idx ++;
全新方法 from y 总
注意:此方法要求原数据无重复!
有点难理解,但还可以
The key Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
int a[N], p[N];
// 其中 a[i] 表示原数据数组 p[i] 表示 a[i] 的相对大小次序,即 p[i] 即为 a[i]
// 将 a[] 进行 1~n 的离散化并将其赋值到 a[]
void work(int a[])
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
sort(p + 1, p + n + 1, [&](int x, int y) {
return a[x] < a[y];
});
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) a[p[i]] = i;
}
解读 sort():sort() 之后有$a_{p_1} < a_{p_2} < \cdots < a_{p_n} $